Introduction
Welcome to a realm where walls listen and lights respond – the world of smart homes and ecosystems.
In today's digital age, it takes more than a vision to create a technological marvel of a home or building; it takes an orchestra of technical expertise and a team of experienced professionals from a variety of fields to bring that vision to life. Software developers weave lines of code like intricate melodies, hardware specialists sculpt the tangible elements that make homes intelligent, AI and IoT experts instill learning and adaptability in these spaces, and cloud computing specialists ensure that everything syncs harmoniously.
We couldn't find relevant and useful information while searching for Smart Home system development details. That's why we've put together a series of articles that cover every aspect of Smart Home ecosystem development.
We will figure out the complexities of their inner workings, investigate the reasons for their rapid rise in popularity, and shed light on the many steps involved in their development.
This article discusses the essentials that make a home intelligent and how to build an intelligent home, which meets the requirements of today's demanding consumer in the society. In the next pieces, we'll break down each component in greater detail to give you the best “how to make a smart home” guide possible.
If you don't want to miss the upcoming article on Smart Home System Development, subscribe to our newsletter right now.
1. Smart Home Concept And How Does It Work?
Entering into the world of smart homes is more like stepping into a blank canvas where innovations contribute to painting the future. The idea, the unfinished masterpiece, but already with such an extensive array of gadgets and systems that can promise us homes full of comfort, convenience, and safety.
Essentially, think of it as a combination of devices and systems, all connected by the internet or a local network. This network, referred to as a Smart Home, is more than just levers and knobs, but instead technologies, automation, and some magic.
1.1 A Deeper Look Into The Benefits Of Building A Smart Home
Building smart home ecosystem is all about crafting environment that will suit your end-user needs and simplifying his life. And once we understand the demands, the benefits of smart home ecosystem put on their right clothes, become real, tangible, and easy to reach. Here are some of them:
Convenience: Smart homes provide convenience at your fingertips to regulate various aspects of your living environment remotely. Through just a smartphone screen or voice, the lighting, temperature, security systems, and so many other things can be controlled.
Energy Efficiency: Smart home devices can be programmed to utilize energy in the most efficient way possible, from lighting to other utilities and maintaining set temperatures in homes. Programmability is said to help cut down utility bills as well as open up homeowners to an eco-friendly way of life.
Security: Smart security system helps to monitor events in real-time and alarms. Even we can view security cameras of our home remotely, receive alarms of moments that appear intruder appears, even lock doors from anywhere.
Health and Wellness: Smoke detectors, carbon dioxide sensors and also leakage sensors can alert your phone for responding quickly to danger.
Customization: Smart homes allow personal settings and automation. We can have a morning routine set at certain times of day like turning off the lights, adjusting the thermostat setting at the time when we leave for work.
Remote monitoring: From work, and even when on vacation - you can check the house. Observe surveillance cameras, warnings about suspicious movements and everything will be alright.
Entertainment: How these smart homes connect to entertainment systems harmoniously. We manage audio visual devices, stream the content with an install plan, then enjoy a moment.
Accessibility: Smart devices can be helpful for those with disabilities or problems of mobility, simplifying control of home surroundings due to voice activation or remote controlling.
The concept is fast gaining popularity between consumers, property owners as well as builders of homes with such smart home's benefits. The last set of people would be interested in building a smart house for the reason that it would be a magnet for technology conscious buyers who crave to own state-of-the-art facilities.
As of 2022, the smart home market has exceeded $80 billion, and its growth by another 20% is expected this year. According to the charts of top analytical companies, it's suggested that the markets are bound to grow up by another 300–400% by 2030.
It is worth noting here that a few years ago, such analysts predicted a slightly more mid-sized number - 200 billion in 2030. And as the growing pace increases, we could expect more upwards corrections in our estimates.
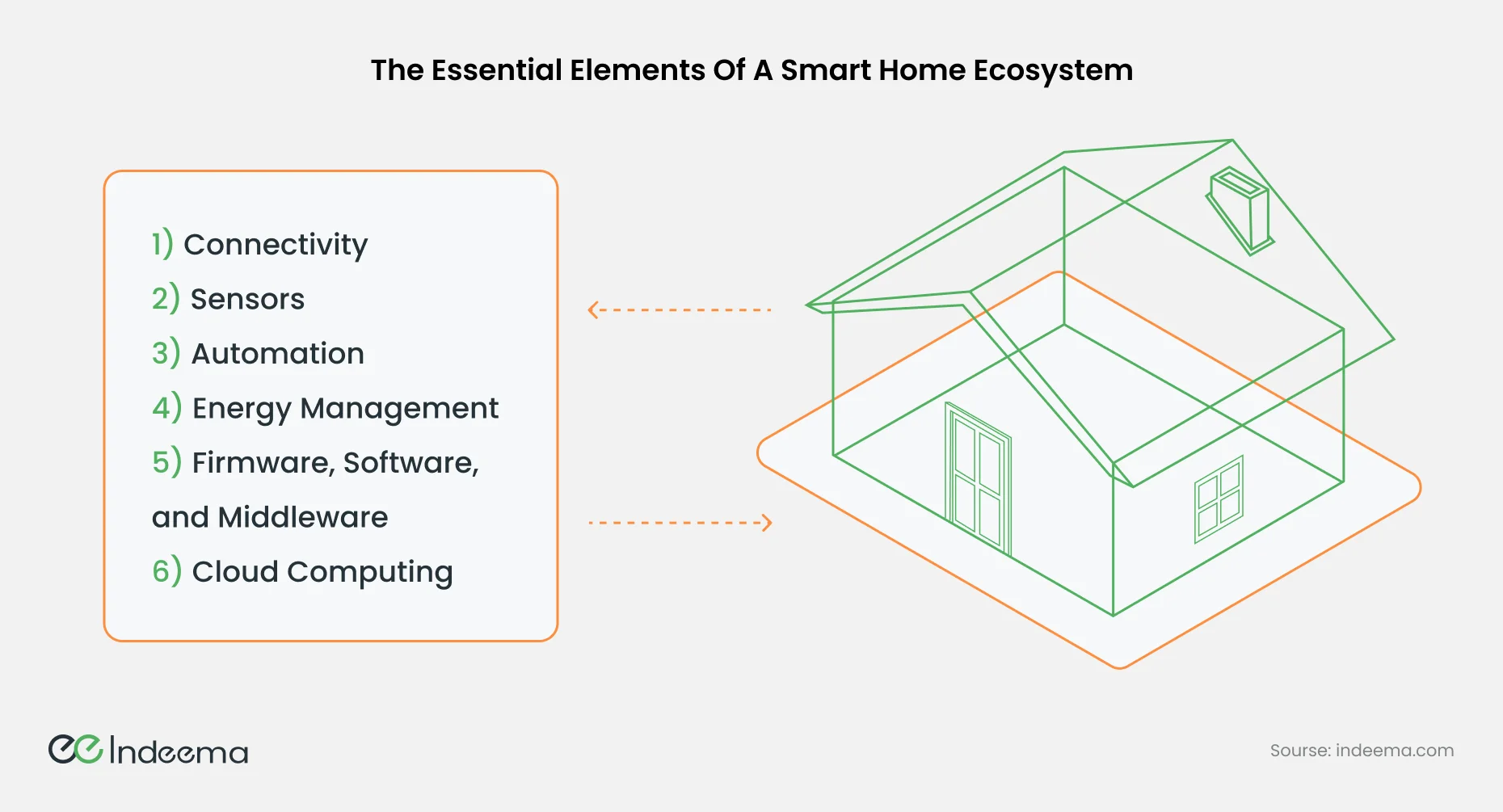
2. What Are the Key Components of a Smart Home?
Now let's get to the good stuff - the heart of the matter. What are the requirements to build a smart home? We'll be breaking down the key components that give a smart home its intelligence.
From the sensors that seem to predict your thoughts, right through to entertainment systems redefining leisure, today's smart homes have it all. That's cool, we knew it, people. But here's the rub – how does it bring everything together?
To answer this question of how to set up a smart home, we shall need to break down the system into the subject components.
2.1 Connectivity in Smart Homes
Therefore, the first theme to consider in the design of a smart home ecosystem is how to connect smart homes. Regardless of smart devices' number we put into our living place, all of them will act as a single entity if not connected to a network.
Stable networking is important for maintaining smooth communication and operation of a smart home ecosystem. A system functions properly if the devices that make up said system, among themselves, communicate and work together. Be it looking around at the other security cameras or cranking up the thermostat, good network connectivity ensures that the commands are executed promptly.
In a few conditions, a wired network could be applied effectively, such as centralized lighting control and connecting stationary smart thermostats along with other devices. This approach will only be feasible during the housing design phase, and implementing this approach in existing buildings will either be too expensive or impossible.
We, therefore, propose wireless smart home connectivity that utilizes wireless protocols that include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and so forth.
- Wi-Fi is the most widespread high-band connectivity protocol. It operates fast and stable so it is more or less impossible to avoid it for media streaming, video surveillance, and smart TVs. However, Wi-Fi consumes more power compared to other protocols, not forgetting it extends difficultly to every corner of the building.
- Bluetooth is more suitable for close-range connectivity but offers less reliability and power. It is a perfect protocol in the smart home connection of close-coupled devices such as smart speakers, thermostats, smartphones, headphones, small IoT devices.
- In particular, Zigbee and Z-Wave are two similar low-power mesh networking protocols; both can produce a self-healing network which still continues in function even though some of devices are not connected. Zigbee is more prevalent in home automation especially through the low-power and mesh networking cases like smart lighting and temperature control. Whiles Z-Wave is widespread in home security systems, smart locks, and energy management. However, both Zigbee and Z-Wave are slower than Wi-Fi and need special coordinators or controllers. Just because setting up either is challenging because of device compatibility (Zigbee) or because frequency bands differ from region to region (Z-Wave).
- Thread is a promising new connectivity protocol developed specifically for IoT and home automation. It is still under development, but has potential for device integration, especially with smart appliances in your household.
Connectivity protocols are of extreme importance in facilitating communications between smart home devices and systems. Each one of them has their defining characteristics, which suit them better for some use compared to others.
2.2 Sensors for Smart Homes and Buildings
The idea of the internet of things is senseless without sensors. So, how to make your home a Smart Home by means of sensors, and why these ones play here a critical role? This is because the smart home ecosystem operates through systemic automation, personalised experiences and increased security enhancing multiple kinds of data that need to be collected in order to enable it as the sensory organs.

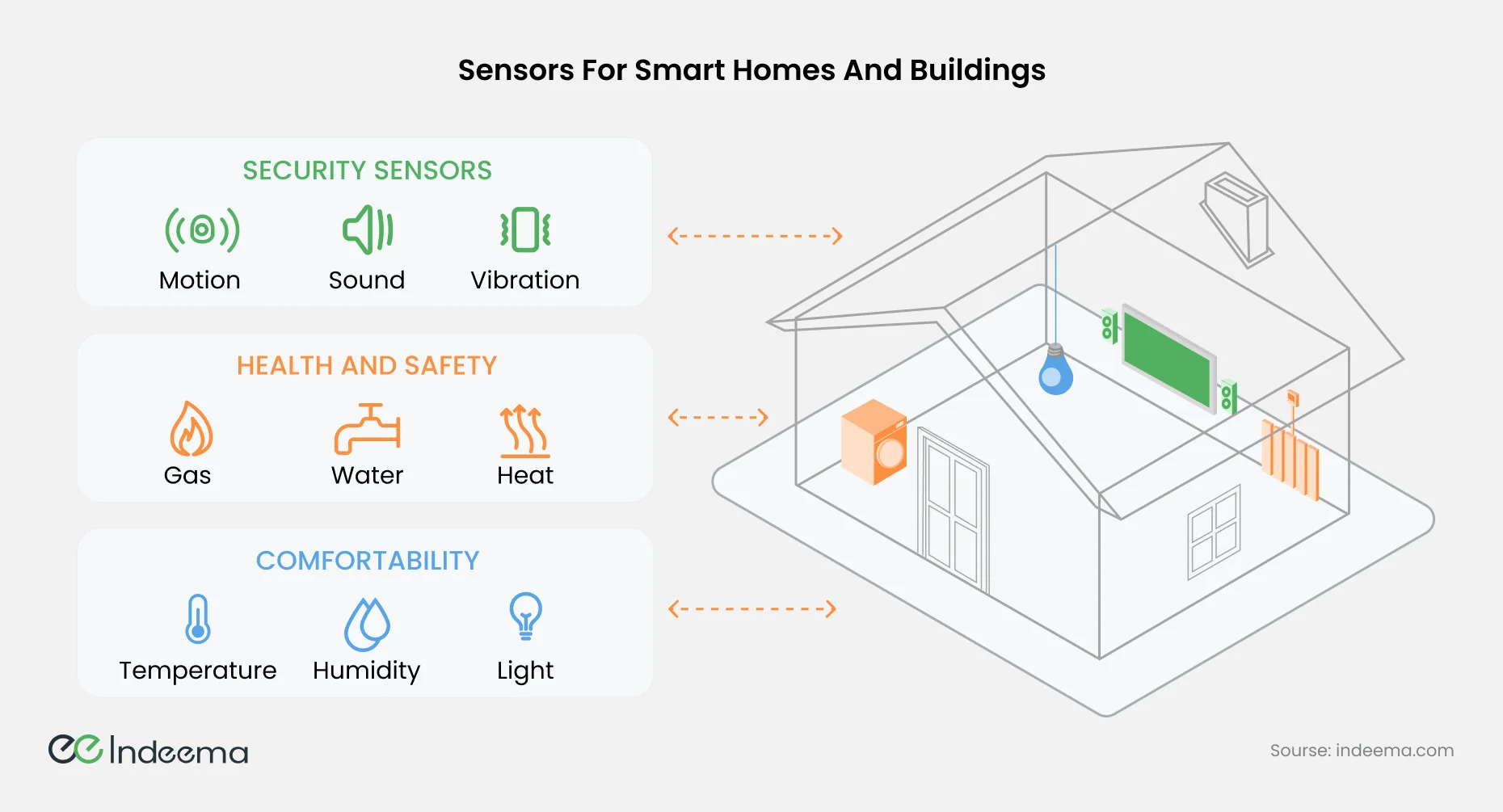
However, before performing development, it is necessary to first identify what are the requirements involved in a smart home's construction and the particularities of such sensors that will be needed according to the functions that will be performed. Some of the many sensors used today in modern smart homes include:
Smart Cameras and Video Doorbells are major tools of the modern home security system which record down not only visual but also auditory data. Other equipment essential besides them includes:
- Door and Window Contact Sensors: to detect opening and closing of doors and windows.
- Motion Sensors: motion and change in motion detection of an object about a given area.
- Sound and Noise Sensors: sound levels measuring and the patterns.
- Vibration and Shock Sensors: vengeance or shock Detecting for burglary alarms, tamper.
A smart home should really take care of the health and safety of its residents. There may be a number of unpredictable situations; burst water supply pipes, fire, and so on. But if the responses are timely - there will be fewer negative consequences. Here are some essential sensors for that:
- Gas and Smoke Sensors: to detect gas and smoke that harmful.
- CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) Sensors: to determine the room's carbon dioxide level.
- Smoke and Heat sensors: to sense smoke as well as temperature increment.
- Water Leak Sensors: to determine moisture, as well as water.
- Flood Sensors: it detects the accumulation of water and elevating itself above the level of danger.
Finally, smart homes assist in comfort and cost-saving in everyday living. In order to make human life comfortable and cost-effective, smart devices are equipped with climate control and energy-saving data collection sensors:
- Temperature and Humidity Sensor: Measures temperature of the surrounding as well between humidity levels.
- Light Sensor (Photoresistors): To detect changes in light intensity.
- Occupancy Sensor: Senses presence or non-presence of people.
- Proximity Sensor: A sensor which either detects whether an object is within observable distance or not to open impulsive doors.
Thanks to these sensors, the location of residents will be regulated in real-time within the building itself, as well as the environment and, accordingly, its lighting. The smart home, using the automation systems, will create the most comfortable conditions for living, while the properties will save resources.
2.3 Automation in Smart Homes
In this case, the collection of data alone will not be in a position to realize full potential out of the smart home. Now imagine the plan to design an amazing smart house. It all boils down to how well Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are choreographed, ingeniously hinted by the word "smart" itself, to create a symphony of automation. These technical feats allow systems to understand data, adapt more easily in new situations and even make good judgments without the aid of laborious programming. Here are examples on how automation is helpful:
- Convenience. Automation removed all those hands-on control of devices. Lights, thermostats, locks, and many others could simply be adjusted by schedules or triggers automatically. Many wireless devices may be executed at once with one command or action from users, which made daily routines become much more streamlined.
- Saves Time. Automation does away with the time being taken to switch lights on and off, regulate temperature, lock doors among other repetitive chores. This enables the user to evade doing that work manually and it can save a lot of time more so when there is alot of tools in the home.
- Security Enhancements. Using AI and ML, the security systems can further be automated to arm and disarm themselves based on user presence or schedules defined by users. The AI and ML can learn what is normal and flag things that seem out of place hence indicating some unusual behavior or a threat to security. The smart cameras may report real-time alerts along with videos when there is motion detection or activity suspicion is happening.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) voice assistants are the best example to put artificial intelligence in use. The most recent versions do not only respond to direct commands, adjust settings or choose a requested music track but also able to retrieve upon the verbal request any information and just chat with the user on the preferred topic. Integrating language models into smart home assistants creates new experiences in their use.
- Customization. While automation allows the user to customize scenarios based on individual preferences, AI takes it another level in the way it has the ability to learn individual user preferences so that personalized experiences are possible. For example, AI may adjust lighting, temperature, and entertainment options according to the variegated tastes of a family's different members.
Automation transforms an ordinary home into an intelligent haven, embodying the core principles of how to build an entire smart home. The artistic stature of AI and ML gives birth to new heights in this automation with the systems now can adapt to new circumstances, take upon new in information and after time unfolds hone its skills to reach the level of proposing alternate strategies for better return on rates.
2.4. Energy Management in Smart Homes
All electronic gadgets, from refrigerators to smartwatches, need charging either by batteries or through the electrical grid. So arises the question of how to build a smart home with minimal energy expenditures. It is interesting to note that smart homes are more environmental friendly due to effective utilization of resources. Besides the fact that it saves money, other than regarding the fact that smart home energy management is also beneficial to the environment by cutting down on carbon emissions being emitted from power plants.
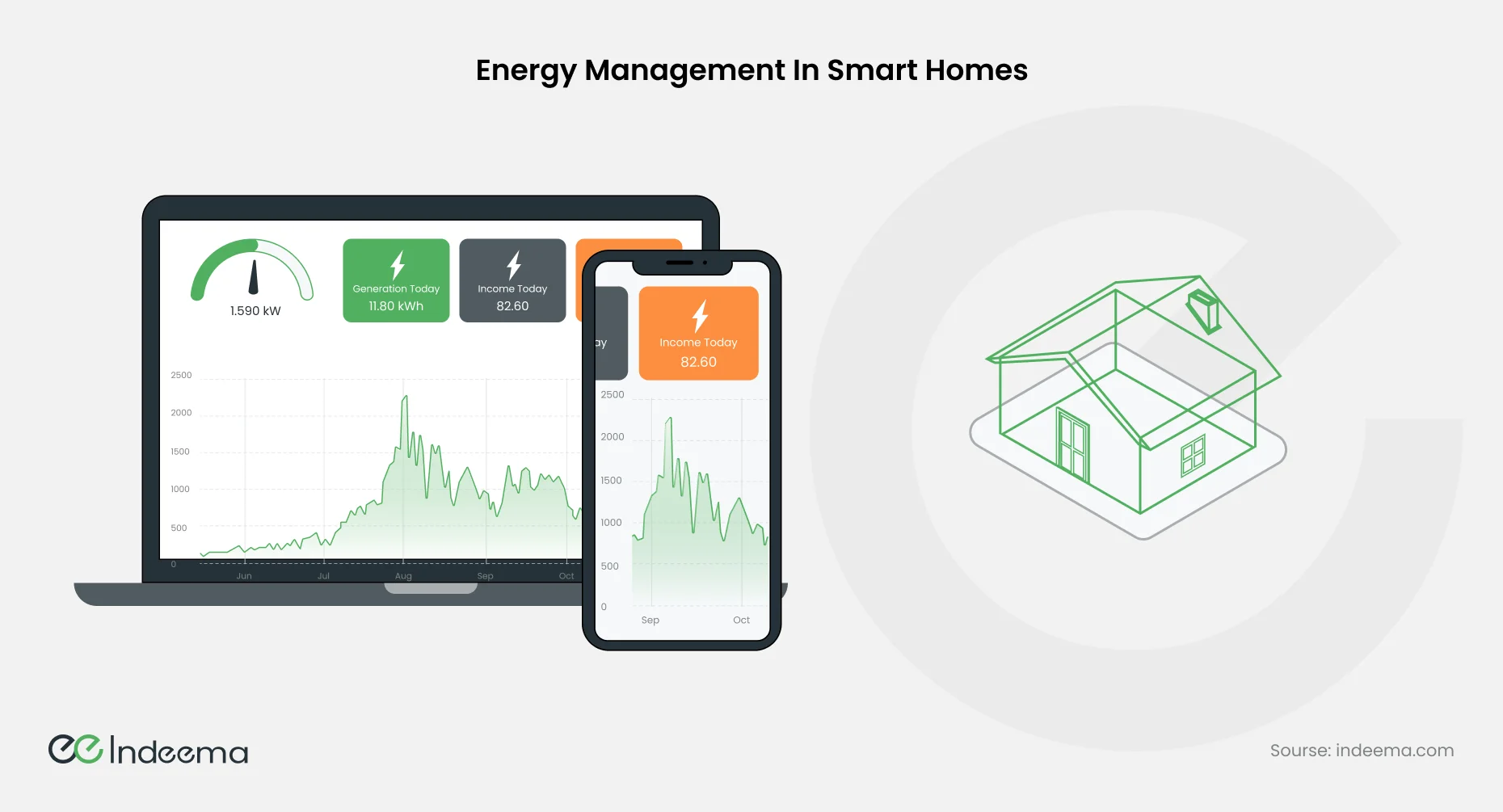
Smart home ecosystem building is aimed to achieve balanced and optimized energy use for homeowners and environmental purposes using data analytics and automation.
Energy monitoring systems are a foundation that makes such homes energetically more efficient. It is a technological application that tracks, analyses, and gives insights to the energy consumption pattern of a given building or home. They do this by use of sensors, meters, and data analytics to give the users accurate information on current energy uses at any particular time.
User can identify the devices which consume power and can make changes in the usage with respect to the devices. AI and ML algorithms can analyze the patterns of usage and the program can make changes in the use of energy. Systems will eventually learn to adjust the settings for the best possible energy saving.
Moreover, your home could turn into an even more greener one or could make money as well. Solar panels, wind turbines, and or other renewable energy sources can be installed within the smart home.
The excess energy can be stored in batteries and or fed back into the grid.
Moreover, smart home could provide the so-called smart grid with information about energy prices, to adjust its consumption and its feeding.
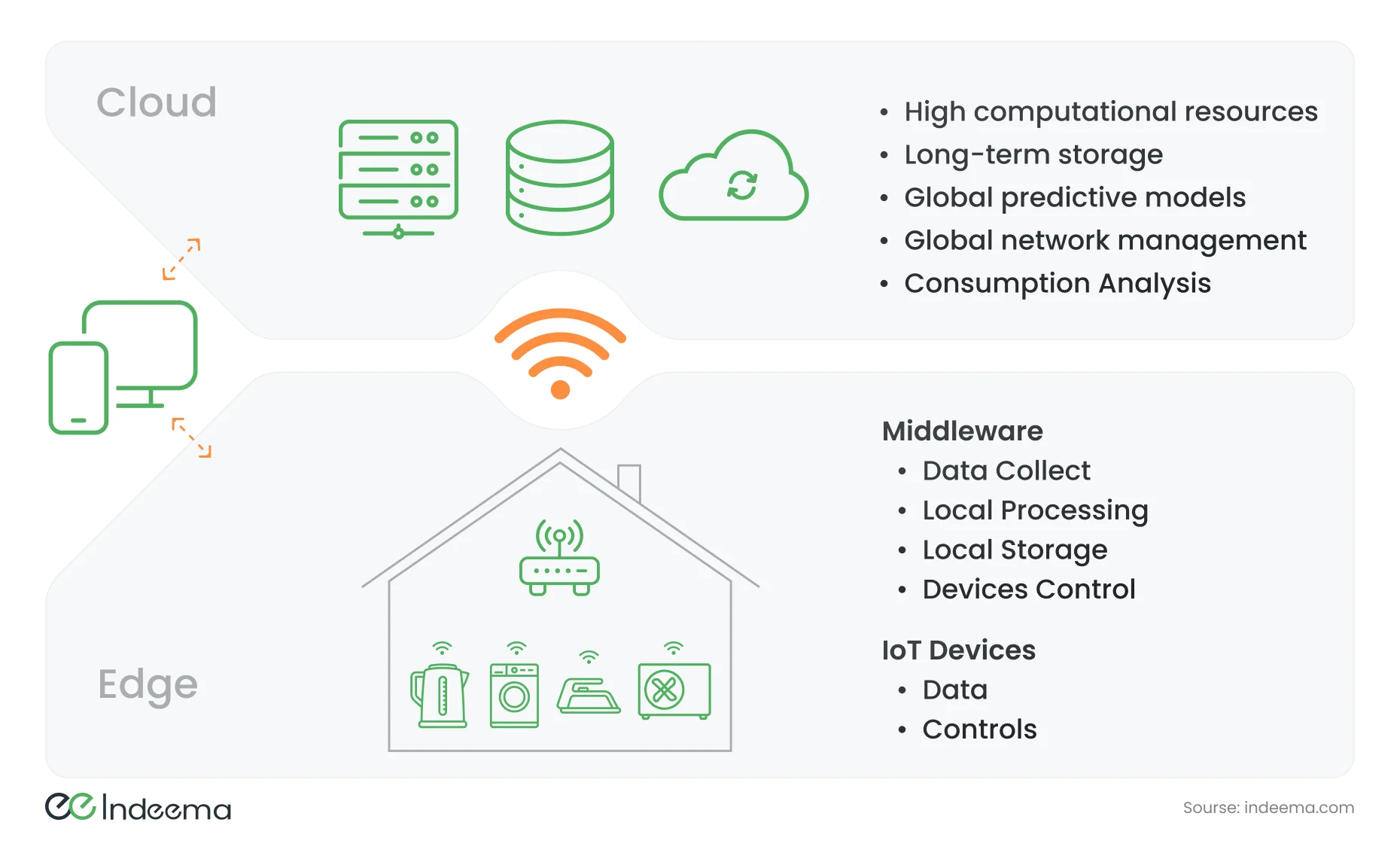
2.5. Firmware, Software, and Middleware
We will not go back and forth. Looking at a big picture, firmware animates hardware while software crafts user experiences and middleware quietly bridges between devices and systems. With this fundamental conceptualization, let us dig into comprehensive exploration of the nuances intricacies to start unveiling.
1. Vital Role of Software in Crafting a Smart Home
The software is another crucial component of a smart home. Traditionally, it consists of three layers which though having their own responsibilities, they all work together in ensuring that devices, applications, and services can operate and interact.
Software applications and user interfaces are important. This includes mobile apps, web interfaces, and desktop software the people communicate with. Thus, along with functionality, a great value here is user experience. Software interfaces allow the users to customize settings, preferences, and automation rules; hence all the settings must be very understandable and user-friendly. On the other hand, home software applications even present an opportunity of automating to some degree routine setup, set schedules, and remotely controlling the devices. The visualizations of data being produced by sensors and devices help the user in better interpreting energy usage, as well as patterns of occupancy or other information.
2. Coding Comfort: How Firmware Revolutionizing Living in Smart Homes
On the other hand, there is firmware that represents low-level software that is put together right into hardware. It is in charge of the operation and management of how the hardware operates.
It controls the behavior of devices like sensors, actuators, and controllers.
Its firmware governs how parts of hardware communicate with each other and also how they respond to the outside world's commands. Firmware may allow features and functions that are not possible on other devices of a similar type, including personalization options or automation routines. These types of firmware updates may be issued by manufacturers to fix any glitches found — relative to the software with which the hardware runs — to fix security vulnerabilities, to add further functionality, or for any reason under the sun.
3. Smart Homes: How Middleware Fuels Complex Operations
Most probably, devices and the software that resides in your smart homes will be from various manufacturers.
Middleware makes things work and lets the devices, apps, and services easily talk to one another and play together. This makes the communication easier and also standardizes the protocols so that different devices developed by different companies can communicate with each other easily. Middleware applies the security controls like secure authentication and encryption that ensures data is safe when it's in transit between the device and the app.
For the experts to write and install smart home software, they are supposed to have a very high level of knowledge about architecture, communication protocols as well as software layers' interaction between them.
2.6. Cloud Computing in Smart Homes
Cloud services integrate smart home ecosystems. They enable the smart homes to have secure and reliable access to the internet, storage and retrieval of data as well as management from a remote place. Here are some of the nice things about the cloud:
- Data storage: Different smart home devices may collect a huge amount of data, in which cloud services foster its collection. This data may foster energy usage tracking, behavior pattern identification and predicting human necessities in the near future. Data is always stored in the cloud regardless of the device's operation, and efforts will be made to restore the data should any type of data loss occur. This is a particular advantage in the case of security cameras, as intruders often target them first.
- Data processing: This is referring to the use of cloud services to process data harvested from the devices in a smart home so that it can give recommendations. For instance, the cloud service can help in coming up with goods and services that a user would like to have.
- Communication: Cloud services could synchronize information across different platforms and devices. One would perform an activity on a device and reflected the same action in relation to other connected devices, hence making the experience for every user similar.
- Scalability and other key benefits of cloud-based solutions for smart home systems, enhanced security, convenient access from any location. The number of connected smart home devices to the internet is growing quickly and the cloud services are well positioned to be able to scale and change accordingly. The data is continuously protected and synchronized in such a way that the same can be used for an analysis saving at the same improving on the system performances.
There have been valid concern regarding cloud-based smart home solutions for having stored crucial user's life information classically regarded as private and sensitive. That is exactly what makes it important to include a cybersecurity specialist into the team of smart system development and provide support in the process of the developing design.
By further incorporating encryption parameters and trust verification more on a device level, unauthorized data access is effectively minimized apart from cases where social engineering methods are thought to be considered.
3. Smart Devices That Make Our Homes Smarter
While investing in smart devices may have a cost at the beginning, but many homeowners consider that long-term savings benefits with energy bills, less maintenance, and even more efficient home compensate for the primary expense.
Smart home ecosystems are modular in nature where homeowners can start small and get bigger. With the passage of time, the new devices can be added to the home as we desire. In our next article, we shall try dwelling deeper into the Smart Home Devices like the complex hardware part found in the IoT devices. For now, let's focus on what are the top smart home device options available to the consumers at present.
3.1 Smart Thermostats
Gone are the days when one would have to manually adjust thermostats. Popular current smart thermostats like Nest and Ecobee have been designed to get your temperature preferences, not mentioning they can be remotely controlled through smartphone apps.
3.2 Voice Assistants
Smart speakers powered with voice like Amazon Echo and Google Home are not limited to only playing your favorite songs, but they answer you back, control other switches or devices, and even predict weather updates.
3.3 Smart Lighting
Smart lighting systems like Philips Hue and LIFX allow adjustment of brightness, colour, and scheduling allowing one to mold the lighting in your home to any occasion or mood.
3.4 Home Security
Ring Video Doorbell and Arlo Cameras are gadgets that help with real-time video surveillance and motion detection, which push through notification to your phone, in case there's something wrong.
3.5 Smart Locks
And, with smart locks, you also leave behind the days of frantically searching for keys to get into your house. Brands like August and Schlage even offer keyless entry via smartphone apps or PIN codes entered on the keypad. You can even provide temporary access for your guests.
3.6 Smart Plugs
The TP-Link Kasa and Belkin Wemo are two easy devices that will turn your regular appliances and electronics into ubiquitously smart, internet connected devices.
3.7 Smart Appliances
From refrigerators taking tabs on groceries, to being able to control a washing machine in some other room, those appliances are game changers. Another tip is running the appliances during those non-peak hours as well helping save the energy costs.
Building smarter, better connected home is an increasing trend that is likely to do nothing but accelerate as the technology continues to improve and newer, more effective solutions come to market.
Let Our Technology Experience Drive Your Business Forward.
Conclusion
In conclusion to our discourse on home smartening how to make, requires high level of expertise that the end user will expect in building a smart home ecosystem. Another aspect to underline is the rapid evolution that exists in the smart home sector. A natural brutal one, noting the fact that system requirements can vary from what initially they were to how they are implemented. In this regard, it is rather important to consider attentively what kind of changes may occur and be ready for adapting to new skills such as innovative sensors or the most recent approaches of artificial intelligence.
Though, a complete solution that can govern to every daily household task is still hard to find but many possibilities are on the horizon which can think of implementing by the consumers in near future. We believe that our smart home guide will help you answer the question of how to build a completely smart home.
