Introduction
Technology has always been at the heart of military affairs. According to history, the majority of battlefield victories were achieved by utilizing the strengths of military equipment. In ancient times, the best small arms and armor were cavalry and siege engines.
The invention of firearms, the presence of which incredibly fuelled the army of any country, radically changed the principles of combat. The next change in military affairs came with the arrival on the battlefield of the Industrial Revolution, which brought such military equipment as tanks and aircraft. The development of technology has led to the emergence of weapons, the range of which is limited only by the size of the Earth, and the damage global scale can be simply incredible. In fact, the weapon had reached its peak. But not technology. Industry 4.0 came onto the battlefield and changed all the rules again.
According to a 2022 GlobalData research paper titled ‘Internet of Military Things’, it is not possible to estimate the precise size of the IoMT market as many devices and IoT in military applications being researched and developed are sensitive, but it provides overview numbers using the global IoT market and gleaning those civilian solutions that can be used by IoT in military and defense. You can also consider How to Investigating Vehicle Telemetry - What It Is, Why It Matters, and What Lies Ahead.
The military applications of IoT technology, or as it is called, the Internet of Military Things (IoMT) or the Internet of Battlefield Things (IoBT), is hard to overestimate. IoT tools and devices are integrated into almost all aspects of military affairs in modern armies.
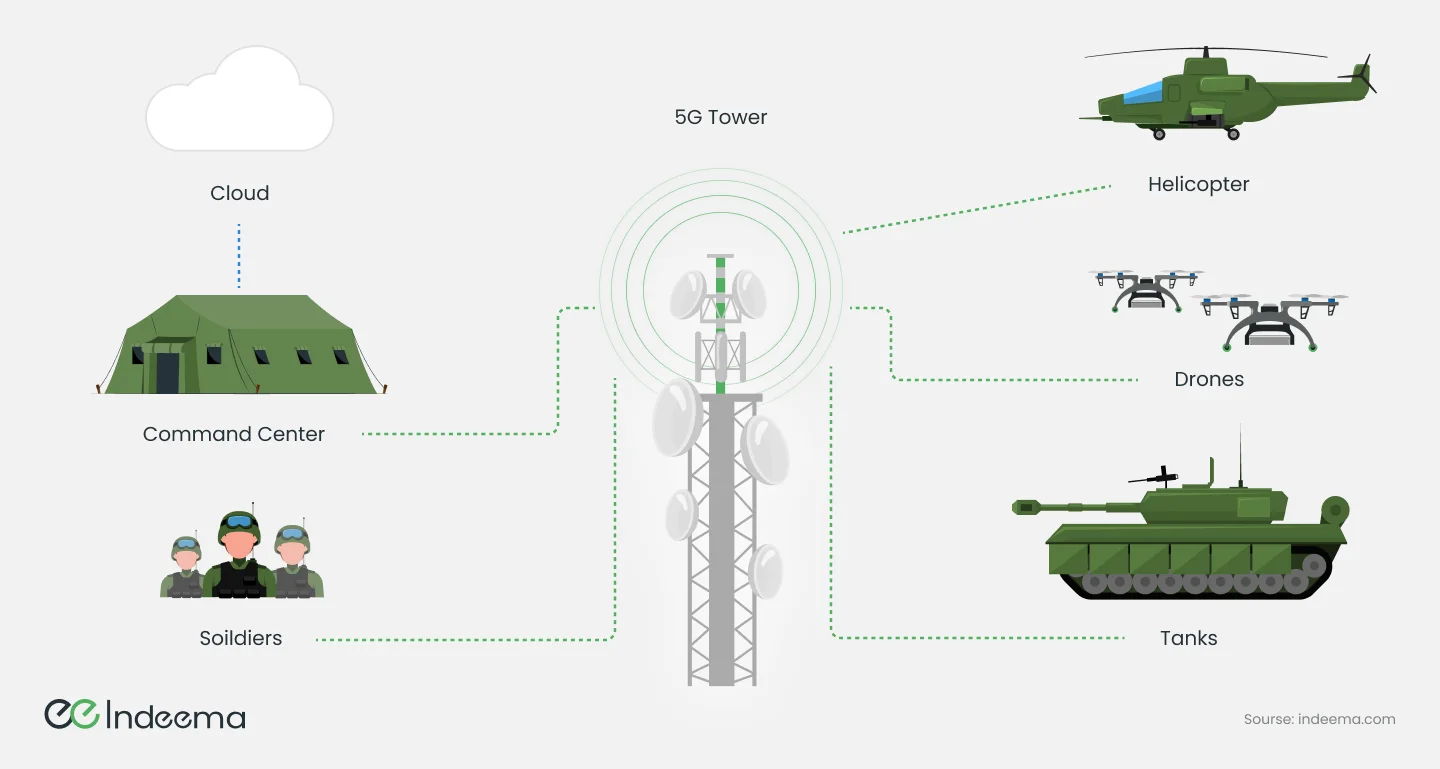
Despite the absolute comprehensiveness of their use, there are a few areas: intelligence, logistics, and health.
1. IoT for Healthcare and Military Medicine
The life of every soldier on the battlefield is precious, so it is not surprising that much of the use of IoT in military is related to the health and survival of combatants. Most modern technologies and means of artificial intelligence are concentrated on the soldier.
1.1 Monitoring Devices
Continuous soldier health monitoring is a crucial task in combat. Unlike everyday monitoring devices, such as fitness trackers, complex systems are built for the military and consist of dozens of sensors integrated into a soldier's clothing. Such devices can also collect operational context data analytics. Together, these data not only determine complete information about the state of health but also allow for assessing the psychological state of a person or identifying a fighter on the battlefield. The continuous flow of data received by the command center from the soldier's wearable connected sensors allows the identification of health problems before a person feels them and the provision of necessary medicine to the soldier, as well as the soldier's removal from the battlefield if necessary.
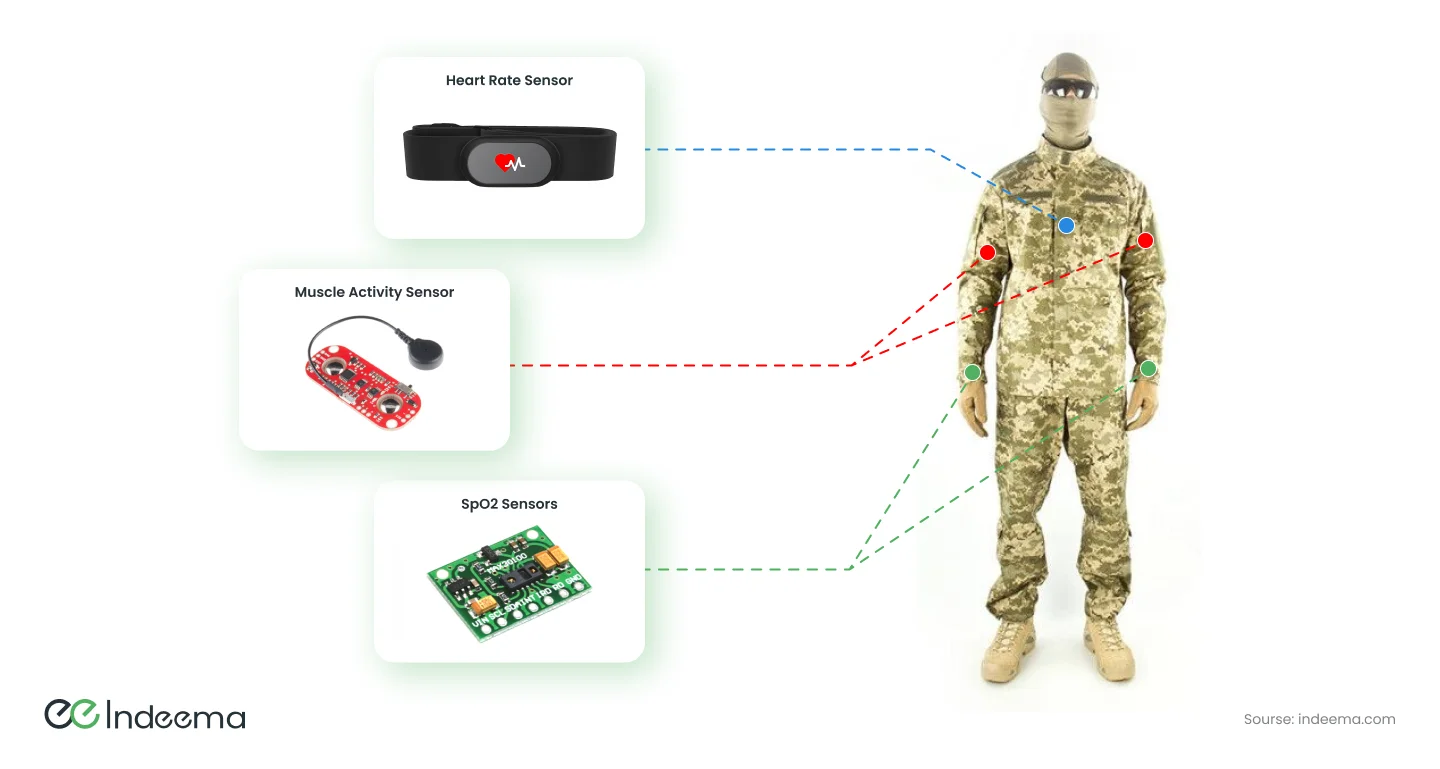
In cases of injuries, medical data helps accurately determine the necessary equipment needed to save a soldier's life and prepare it in advance. This approach increases the efficiency of military medicine and medical logistics. At times, all of these factors work together to reduce battlefield losses.
In asymmetric warfare, it isn’t always easy to identify enemy combatants. Models of human movement and behavior are built according to the data collected from the fighter's body. Complex models as indicators can be used to identify the warrior on the battlefield, even without direct contact with him.
Also read the article as How to Building a Web Platform for the Health and Wellness Industry.
1.2 VR and AR Equipment
Troops use the data collected during combat operations and the models obtained in this way in other areas as well. For example, from the received real data sets together with recordings from body cameras, build the virtual world for the training of the next generation of soldiers. In this way, a virtual model of the combat world with conditions as close to reality as possible is obtained. By training with VR and AR equipment, soldiers can improve accuracy, combat tactics, etc. without the possibility of physical damage. Indeed, during training, mistakes may take place, and the same situations during the fight might last a lifetime.
The use of virtual reality in the training of aircraft and helicopter pilots is particularly effective, as training in conditions close to combat for this category of soldiers is associated with extremely high risk.
2. IoT for Military Logistics
The next most important task after saving a soldier's life and health is logistics. The basis of victory in modern warfare is the rapid and efficient allocation of resources. Troops cannot win the battle if they do not have enough machinery, equipment, ammunition, fuel, and food right there when they are needed. The dynamic change of circumstances on the battlefield does not allow for calculating in advance all possible options for the events developing, and therefore it is necessary to respond in real-time. And here the Internet of Things comes in handy again. The military is increasingly using an IoT army to gather intelligence and carry out missions.
More than half of modern military equipment consists of electronics. Part of these electronics are environmental sensors of state and position. The service life of engines of heavy equipment, such as tanks or self-propelled units, is limited as engine construction must be small in size and efficiency.
Continuous monitoring of engine condition, fuel consumption, and quantity, and real-time GPS tracking with the use of artificial intelligence allow staff to accurately determine the right moment to repair or replace an engine or other equipment with limited resources. The use of artificial intelligence systems on board vehicles, including naval ones, can minimize fuel costs for transporting people and equipment. Real combat data show that fuel savings can reach 25%. And delivering explosive fuel to the battlefield is always dangerous. Therefore, this approach not only reduces financial costs but also helps with safety.
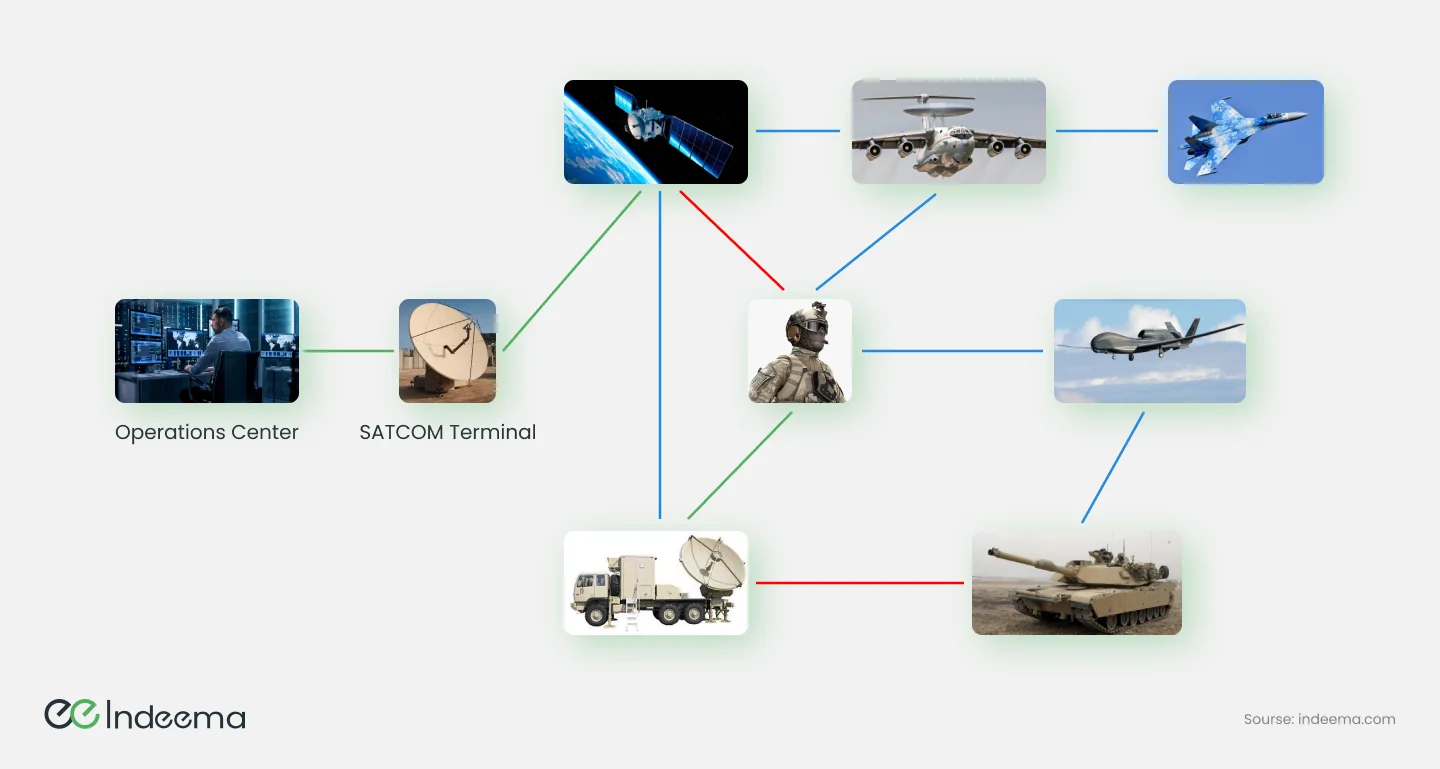
Efficient transportation and thermal distribution of goods is another important task of logistics. Weapons, tanks, cartridges, and many more instruments are necessary on the future battlefield, so they must be delivered on time and without delay. But the goods should not be delayed in warehouses, because then the accumulation points become good targets for the enemy. RFID tags are effectively used in the army to monitor the movement and accumulation of goods. We have already talked about this technology and its prospects for logistics in our article. RFID tracking helps effectively build supply chains.
Application to the flows of goods by centralized AI enables allowing military personnel to forecast which products are in demand or in excess. This approach optimizes logistical control and helps to avoid losses due to robbery and sabotage. It should not be forgotten that civilians may need to be evacuated from hostile areas or food delivered to the remaining people.
Therefore, an efficient transportation map should be built to avoid congestion. Continuous monitoring of transport flows by GPS and RFID tracking of goods and vehicles helps to build complex delivery schedules in real-time, so achieving the efficiency of the delivery structure is unattainable in the case of manual control.
Explore Our Success Stories.
3. IoT for Exploration of the Area
Analysis of the region, where the battle will occur, and the forces of the enemy have always been the basis of military strategy and tactics. Modern, high-technology spy satellites placed in low Earth orbit construct a global map of the area and estimate the total amount of enemy equipment. They can photograph the area with high accuracy and in different wave ranges with highly efficient sensors. This helps to assess not only the presence of enemy armed forces and their coordinates but also to determine whether the equipment has moved recently to assess the presence of a nuclear threat. The forces used some techniques to deceive satellites, like plastic models of equipment and visual camouflage. The main problems of satellite reconnaissance are its remoteness and its not-changeable trajectory.
The satellite moves in a stable orbit and is above the battlefield only for a limited time, so it is impossible to count on operational data about the dynamics of the battle. Previously, specialized reconnaissance aircraft worked on the battlefield; they circled over a given area and assessed the topology of the region, the availability and position of equipment and enemy forces, and the relative coordinates of friendly fighters. Currently, various modifications of airborne drones with connected cameras are performed for these tasks.
These are aircraft of various weights and shapes that can operate at a distance of 10 to 300 km from the operator. Therefore, operational data on the state of the battlefield can be obtained without danger to the person operating the device. Drones use built-in sensors, cameras, and software to build three-dimensional maps of the terrain, determine enemy positions, and transmit those positions to the command center, where officials are able to make strategic judgments using this information. These drones may also be utilized for automated control of the battlefront or border, even without human intervention.
When suspicious activity is detected, the drone sends a signal to the base, where the information is checked by the operator, who then takes control.
4. Communication With the Help of IoT
As you can see, IoT military smart devices effectively help to save the lives of soldiers. But the continuous work of such a complex system is possible only with constant and uninterrupted communication between other connected devices, soldiers, warehouses, vehicles, equipment, operators, and the command center.
Altogether, it must work as one complicated mechanism, so breaking the link between its parts can reduce efficiency or even disable it. For dozens of years, the most stable and uninterrupted method of data transmission was the wire one, but for modern combat operations, such an approach is not only outdated but also impossible. Most other biometric data transmission today is via encrypted radio transmission, similar to that used by common IoT.

But, as we wrote in our article on Starlink, the global use of satellite communications has greatly simplified the maintenance of the military information infrastructure, as such data transmission is mostly impossible to stop. An enemy can use special jamming stations, which create radio interference, to suppress satellite and other radio communications.
However, as the practice of using the same Starlink in the war in Ukraine has shown, due to the dynamic change in the frequency range, such enemy defense systems have proved less effective
5. Why IoT is Essential for the Future of Military Operations
Military devices are becoming smarter to ensure fewer casualties. It is difficult to determine exactly how much money is spent on the military IoT because some developments in this area are classified.
But experts estimate that the military IoT accounts for 7%–11% of the total Internet of Things market. These include body sensor systems, vehicle electronics, targeting systems, unmanned aerial vehicles, and so on. In modern warfare, not only reconnaissance but also strike drones are actively used. These include ground, waterfowl, and aircraft devices. Percussion drones have a special, effective light weapon on board that allows you to damage the enemy when performing reconnaissance operations. Or the drone itself can be an explosive device — a kind of guided war missile with a reconnaissance function. The drone operator is in a safe, protected area without having to move to the war front.
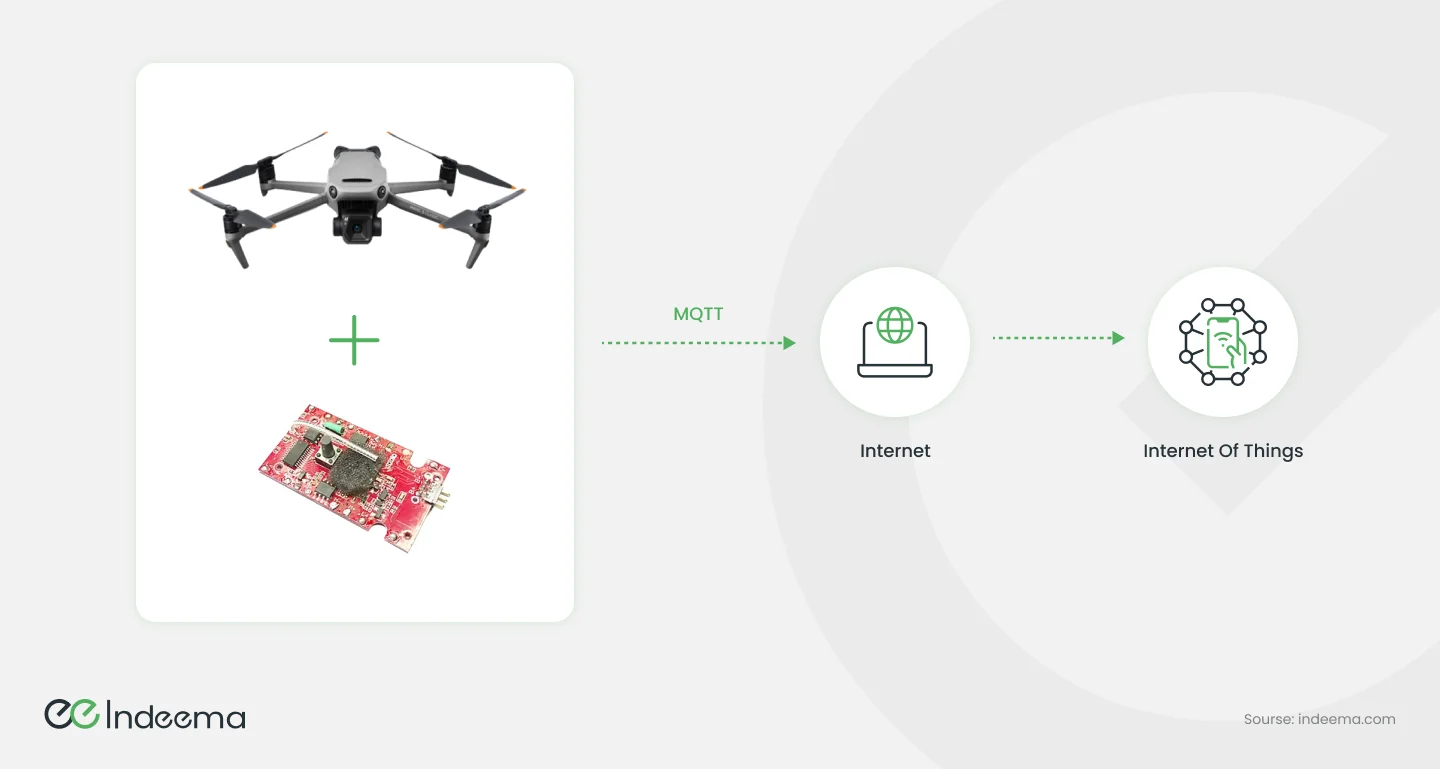
Simultaneously, the main systems of the device perform non-core functions, such as course maintenance, target identification, and so on. Thus, with the development of AI systems, one operator will be able to control several unmanned devices. In fact, this is the basis of the concept of future war. Man, the soldier, is the most valuable in the modern army, so with the help of technology, including the
Internet of Things, the military around the world is trying to protect him. And the best way is to pick up a soldier from the battlefield. For example, some NATO countries are already developing aircraft carriers with a strike group of unmanned aerial vehicles with weapons systems similar to conventional combat aircraft. And the advantage of this approach is obvious.
Let Our Client Success Stories Inspire You.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, humanity will probably never get rid of the habit of fighting. But future wars not just can, but must move to a new level. The approach should disappear when the main victims of aggression are ordinary civilians in astronomical numbers. Strikes must be inflicted exclusively on enemy military targets without harming ordinary people. But while some countries like Russia are fighting on the old principles and demolishing entire cities with their populations, there are people who simply were not where they should be and did not have time to escape. But a civilizational approach and modern technology must help stop the aggressors.
Related: How to Set Up and Connect Your Car for the Internet of Vehicles
