Introduction
With the rise of IoT, mobile applications have emerged as a crucial tool for managing and interacting with IoT devices. In our previous articles, we have already discussed the benefits of using IoT mobile apps and provided guidance on creating them.
Integration of the Internet of Things into daily life is inevitable. In fact, it's already occurring. Taking a moment to consider the devices that surround us – fitness trackers, infant monitors, smart door locks – reveals that Internet of Things applications are pervasive. They are increasing productivity, enhancing convenience, and occasionally making us feel as though we are living in a science fiction film. In actuality, there are approximately 15 billion IoT-connected devices, and the number is expected to exceed 29 billion by 2030.
In this article, we take a closer look at real-world examples of IoT applications and explore how they are being used in different industries. By examining some of the most innovative and effective examples, we can better understand the potential of IoT mobile applications.
In addition to exploring real-world IoT mobile app examples, we will also share our own case study of developing a mobile IoT solution for monitoring air quality. We will detail the challenges we faced, the stages of the development, and the outcomes we achieved. By sharing our experience, we hope to provide valuable insights into the development process of IoT mobile apps.
2. Understanding IoT Device and Mobile App Connectivity
Understanding the relationship between IoT (Internet of Things) smart devices and mobile apps is critical for developing successful and efficient mobile IoT solutions. Various communication protocols and IoT technologies are generally used to connect IoT enabled devices to mobile apps. Let's look at the most important features of this connection:
1. Protocols for Communications:
- Wi-Fi: Many IoT connected devices communicate with mobile apps via Wi-Fi networks, which enable high-speed internet access and a consistent connection. Smart thermostats and security cameras are two examples.
- Bluetooth is frequently used for short-distance communications, such as linking a smartphone to a wearable fitness tracker or smartwatch.
- Zigbee and Z-Wave are wireless protocols that are widely used in home automation IoT systems to connect wearable devices such as smart lights, locks, and IoT sensors to mobile apps.
- Cellular connectivity (e.g., 4G/5G) is incorporated into some IoT devices, allowing them to connect directly to mobile networks without relying on Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. This is useful for GPS trackers and remote sensors.
2. Gateways and hubes:
If IoT devices employ different communication protocols, a central hub or gateway can aggregate data and give a consistent interface for the mobile app. This hub acts as a conduit between multiple device protocols and the app.
3. Cloud Services and APIs:
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are commonly used by IoT devices to communicate with mobile apps. APIs are created by app developers to allow apps to send commands to devices and retrieve data from them.
- Cloud services are frequently used to help IoT devices and mobile apps communicate with one another. Devices deliver data to the cloud, which the app can access via APIs. IoT devices can also be managed and updated remotely via cloud services.
4. Security and authentication:
In IoT networking, security is a vital factor. Authentication measures must be used in devices and apps to ensure that only authorised users can manage devices or access data.
Encryption is used to protect data exchanged between devices and mobile apps, preventing data breaches and eavesdropping.
5. Data and notifications in real time:
IoT devices frequently transmit real-time data to smartphone apps. Sensor readings, status updates, and warnings are examples of this data. Mobile apps must process this data quickly and offer consumers with timely notifications.
6. User Interfaces (UI):
The user interface for controlling and remote monitoring IoT devices is provided via mobile apps. They can include functions like remote control, scheduling, and data visualization.
Responsive design is required to ensure that the app operates properly across a variety of mobile devices and screen sizes.
7. Power Control:
The power needs of IoT devices vary. Some are battery-powered, while others must be plugged in. These devices' power status may require mobile apps to monitor and regulate.
8. Interoperability and scalability:
Mobile apps must be designed to scale smoothly as the number of IoT devices increases. Interoperability between devices from different manufacturers is also essential for providing a consistent user experience.
9. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates:
OTA updates for IoT devices may be enabled via mobile apps, allowing manufacturers to remotely improve device functionality, address issues, and strengthen security.
10. Analytics and Data Storage:
Mobile apps can preserve historical data from IoT devices and offer analytics features to assist users in making informed decisions based on prior performance and patterns.
Understanding and controlling communication between IoT devices and mobile apps is critical to developing dependable and user-friendly IoT solutions. The effectiveness of these interconnected systems is dependent on effective communication, security, and user interface design.
2. Discovering the Top IoT Mobile App Ideas: Real-World Examples
Understanding the most recent trends and advancements in the mobile application IoT market can help in our understanding of the features and functionalities that users of IoT mobile applications demand.
Microsoft's "2019 Manufacturing Trends" report indicates that in recent years, the implementation of IoT solutions has become easier for businesses, thanks to the availability of affordable and dependable sensors and multiple devices. Furthermore, the demand for mobile IoT apps has been driven by the ongoing digital transformation of various industries.
The potential for IoT mobile app ideas is vast and varied, with countless opportunities for innovation. Therefore, it is worth exploring some of the most well-known examples of IoT based mobile apps across different industries.
2.1 Home Automation
The Nest app, SmartThings, and Amazon Alexa are some of the most popular IoT mobile apps in the home automation industry. These apps allow users to control their home's lighting, heating, security, and entertainment systems remotely using their mobile devices.
2.2 Wearables and Fitness
Fitbit, Garmin, and Apple Health are some of the most popular IoT mobile apps in the wearables and fitness industry. These apps allow users to track their physical activity, sleep, and nutrition.

2.3 Personal Health Monitoring
Philips HealthSuite, Omron Connect, and MyChart are some of the most popular IoT mobile apps in the personal health monitoring industry. These apps allow patients to track their vital signs, manage their medications, and receive guidance on managing their health.
2.4 Retail
The Amazon app and Walmart app are some of the most popular IoT mobile apps in the retail industry. These apps allow users to shop for products online, track their orders, and receive personalized recommendations.
 (1).webp)

2.5 Agriculture
The John Deere Operations Center app and the Climate FieldView app are some of the most popular IoT mobile apps in the agriculture industry. These apps allow farmers to monitor their crops, manage their equipment, and receive insights on optimizing their operations.
2.6 Transportation
The Uber app, Waze, and Google Maps are some of the most popular IoT mobile apps in the transportation industry. These apps allow users to request rides, navigate to their destinations, and receive real-time traffic updates.
3. Case Study: UBreez IoT App - Remote Air Quality Tracking
With the advent of IoT technology, there are numerous IoT mobile app ideas that can improve people's lives. One such example is the UBreez product developed by the Indeema team.
We discovered that indoor air quality is a crucial factor affecting our health and productivity. According to ForHealth estimates, improved indoor air quality could save businesses between 25 and 150 billion USD per year. To help address this issue, we have developed UBreez, an IoT mobile application that monitors air quality for both private and business use.

UBreez consists of three components: the UBox device, the cloud platform, and the UBreez application. Using IoT technology, UBreez tracks the quality of the air we breathe by measuring temperature, humidity, pressure, CO2, and VOC levels indoors.
So, let's delve into the challenges faced by our IoT software development team during the development of UBreez and explore the different components of the IoT ecosystem.
3.1 Objectives of the IoT Mobile App Solution
The solution is designed to provide a user-friendly and affordable way to monitor air quality control metrics. The UBreez mobile app is a convenient way to set and monitor accepted levels of air conditions such as temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels. With this app, users can customize their settings and receive notifications in real time if any of the values cross the accepted level.
One of the primary objectives of UBreez is to improve the quality of life for individuals by providing them with a tool to monitor and control their surrounding air quality. This is especially important in urban environments, where air pollution levels can often exceed safe levels. By utilizing the UBreez mobile app, users can stay informed about the quality of air in their homes, offices, or other environments and take steps to improve it as needed.
By maintaining optimal environmental conditions, individuals can reduce the risk of illness and discomfort caused by unfavorable microclimates. This is particularly important for individuals who spend extended periods of time in a single room, such as office workers, students, and individuals working from home.
3.2 Technical Aspects
The IoT project is based on the latest IoT and cloud technologies that enable the device's smart sensors to collect and transmit information from the location where they are placed. This information is then analyzed to ensure the comfort and safety of people staying in the room.
The device is equipped with multiple sensors that measure several important parameters, such as air temperature, relative humidity, pressure level, CO2, and CO2 levels.

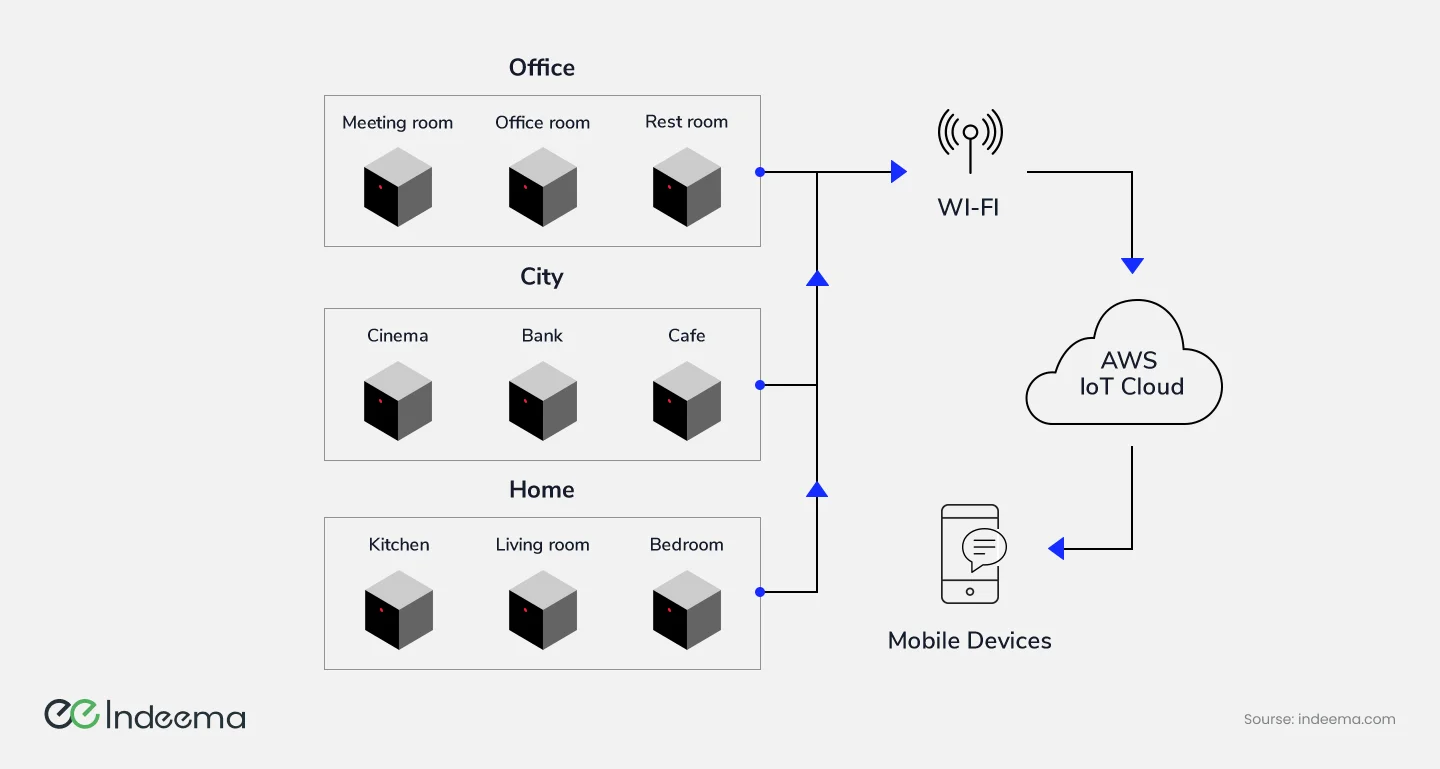

The UBreez platform is based on the ESP32 system-on-chip. The sensors collect data, which is then transmitted to the cloud platform via a Wi-Fi connection. The cloud platform stores and processes this data, making it available to users via the UBreez mobile application.
The UBreez application is available for both iOS and Android devices and is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly.
3.3 Implementation of the Solution
To begin with, the team designed the platform using the ESP32 system-on-chip and a set of sensors. The firmware was developed with the Platform IO toolset for embedded C/C++ development, which enabled the platform to collect data from sensors measuring air temperature, relative humidity, pressure, VOC levels, and carbon dioxide levels. The firmware then sent the data to the cloud via Wi-Fi, using the MQTT protocol.
Indeema's design team followed a user-centric approach to create an intuitive and easy-to-use interface for the UBreez application.
Indeema's development team chose the technology stack that best suited the project, selecting Node JS for the backend and React.js, HTML, and CSS for the front end.
The DevOps team designed and implemented a scalable and secure cloud infrastructure for the Ubreez platform using Amazon Web Services (AWS). They leveraged AWS services such as EC2, S3, RDS, and Lambda to establish a reliable and scalable cloud infrastructure. In addition, they employed GitLab CI\CD to automate the deployment process, ensuring that updates were swiftly and effectively delivered.
The QA team subjected each component to functional testing, integration testing, and system testing, confirming that the IoT product meets the functional and non-functional requirements, as well as being reliable, secure, and scalable.
After the Ubreez project's release, the development team conducted user testing to gather feedback and ensure that the app met user expectations and functioned optimally.
The predictive maintenance stage involved identifying and addressing any bugs affecting the UBreez product, as well as regular updates to the UBreez application to improve its functionality and address any security vulnerabilities.
3.4 Challenges Faced by the Team
Developing an IoT mobile app solution for Remote Air Quality Tracking posed several challenges for the analytics software development team.
3.4.1 Simplifying the setup process
One of the primary challenges was making the initial setup process as easy as possible. This involved creating a streamlined process for connecting the app to the device and ensuring that users could easily customize their air quality settings.

3.4.2 Designing aesthetically pleasing and functional hardware
Another significant challenge was to create aesthetically pleasing and functional hardware. This involved extensive research and development to create a device that was not only effective but also visually appealing and easy to use. The team worked tirelessly to find the right combination of materials, design, and functionality to ensure that the device met the needs of users and was a pleasure to use.
3.4.3 Conducting rigorous testing for precise and timely readings
Thorough testing was also critical to the development process. The team invested a significant amount of time in testing to ensure that the device provided precise and timely readings. This involved testing the device in various environments and under different conditions to identify any potential issues and address them before the product was launched.
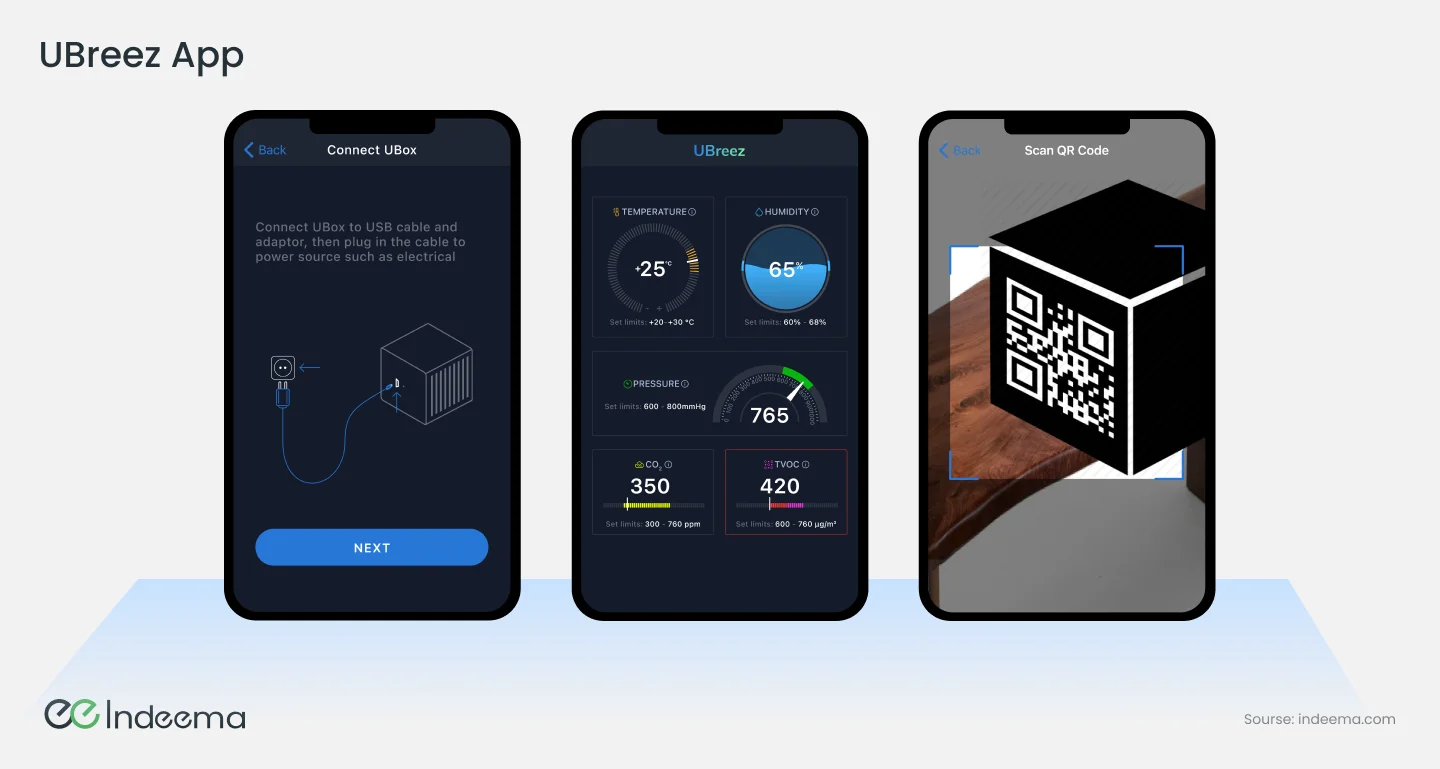
3.4.4 Creating a delightful user experience with applications and UBox
Designing a delightful user experience was another significant challenge. The team focused on creating an intuitive and user-friendly interface that made it easy for users to set up their devices and monitor air quality levels. The app was designed to provide users with all the information they needed in a clear and concise manner, and the team worked tirelessly to ensure that the app was intuitive and easy to use.
3.4.5 Implementing a notification system and binding it
Setting up notifications and binding them was another challenge the team faced. This involved designing a notification system that could provide users with real-time alerts when air quality levels deviated from the accepted level. The team worked to create a robust notification system that would ensure that users could stay informed about the quality of the air in their environment and take appropriate action to maintain optimal conditions.
Overall, developing UBreez, an IoT mobile app solution for Remote Air Quality Tracking posed several challenges for the software development team. However, by focusing on creating an easy-to-use device, the team was able to overcome these challenges and develop a product that met the needs of users and exceeded expectations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IoT technology is rapidly changing the way we interact with the world around us, and IoT mobile apps are emerging as a key driver of this transformation. With the ability to collect and analyze IoT data from a wide range of sources, IoT mobile apps have the potential to improve our lives in countless ways, from monitoring air quality to optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing supply chain management.
As a case study, we explored UBreez, a product developed by the Indeema team that uses IoT technology to monitor indoor air quality. The app provides real-time data on various air quality parameters and alerts users when air quality drops below a certain threshold. UBreez is just one example of how IoT mobile apps can be developed to improve our lives and well-being.

_1683208328163.webp)
