Introduction
The world we live in today has been fundamentally altered by the Internet of Things (IoT). With over 14 billion connected gadgets in use globally in 2022, the IoT seems to be already transforming our environment. Perhaps most crucially, it is starting to play a significant part in the renewable energy sector, delivering hopeful (and much-needed) answers.
In this piece, we'll examine several Internet of Things solutions, such as intelligent distribution and consumption, that are gaining traction in the renewable energy sector, as well as the advantages they provide, including increased control, lower costs, and greater transparency.
1. Importance Of Renewable Energy In The Foreseeable Future
It is difficult to overestimate the impact of affordable energy on our daily lives. This becomes especially evident in the absence of power in the territories like Ukraine, which is affected by war.
The basis of the world's energy is now fossil fuels such as natural gas, coal, and nuclear fuel. But most of these energy sources have finite sources. As a result, most of the world will have to rely on a few suppliers. It's undesirable because the supplier might limit access to resources to serve their motives, including political gain.
Moreover, fossil fuels have a negative impact on the environment. So, using them to produce energy means constant harm to the environment by releasing toxic gases. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources do not produce harmful emissions that contribute to climate change and air pollution. Embracing renewable energy helps mitigate the negative impacts of global warming, reduce carbon footprints, and preserve natural ecosystems.
Moreover, renewable energy sources are typically abundant and widely available. Sunlight, wind, water, and biomass offer vast potential for energy generation across the globe. Harnessing these natural resources can provide affordable and sustainable energy access.
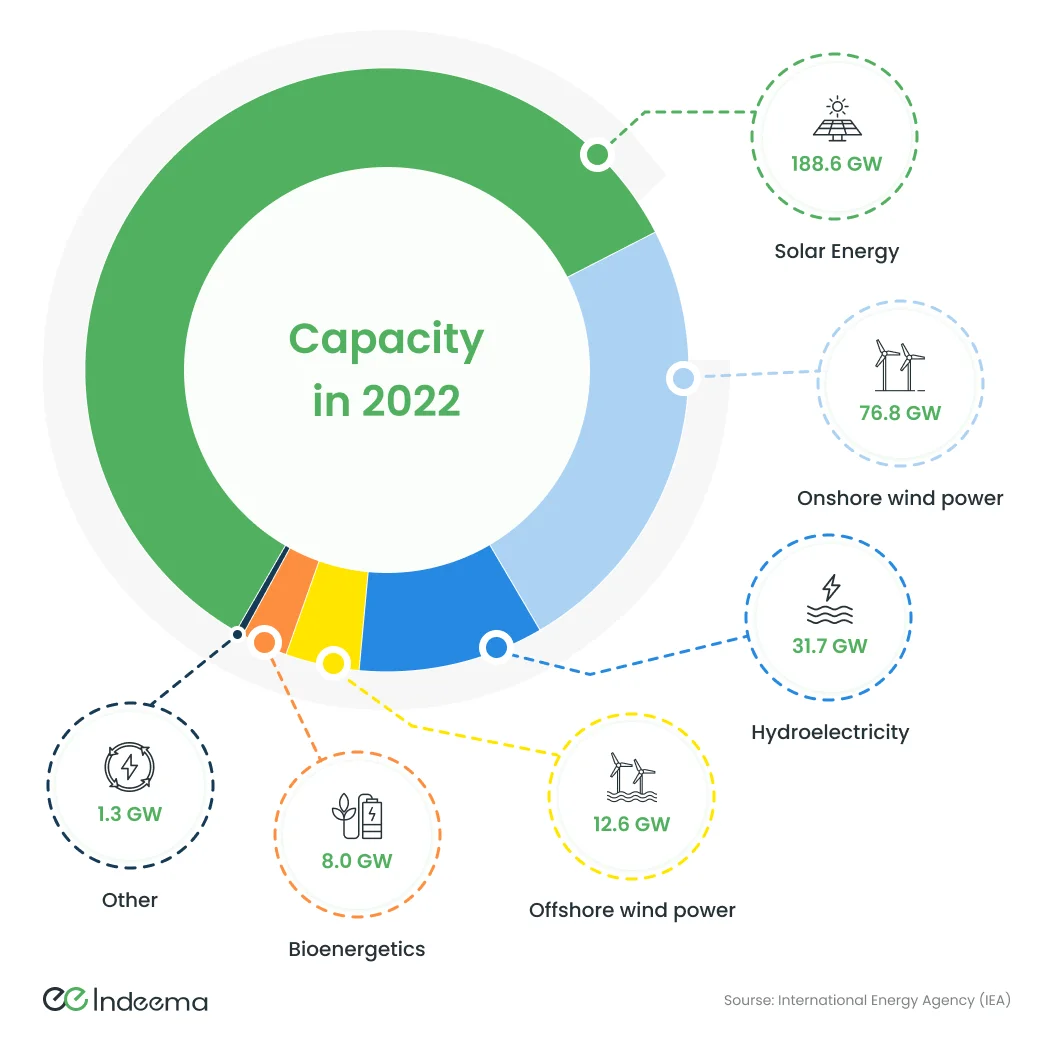
The importance of renewable energy in the foreseeable future cannot be overstated. It offers energy independence, environmental sustainability, technological advancements, and social and economic benefits. Now that we have innovative and less-expensive ways to capture and retain wind and solar energy, renewables are becoming a more important power source, accounting for more than 12 percent of U.S. energy generation.
2. Role Of IoT In Renewable Energy Adoption
Due to their reliance on external influences, renewable energy sources present unique challenges when put to productive use. However, it is possible to overcome this limitation with the help of renewable energy IoT solutions.
2.1 Addressing the Challenges of Renewable Energy: IoT Solutions and Energy Storage Systems
The transition to new, intelligent electricity generation involves the integration of sensors and digital networks. They enable continuous asset monitoring and optimization of power plant maintenance and operations. Hence, the use of AI and IoT in renewable energy production improves the efficiency of conversion processes and collects information for effective decision-making. Specifically, integrating AI agents can significantly reduce downtime by autonomously responding to system faults before they cause outages.
With the help of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, anticipation and effective localization of problems and equipment failures optimize employees' work and increase electricity generation's efficiency and reliability. On the other hand, continuous monitoring of remote resources reduces maintenance costs.
But the biggest problem of all renewable power sources is the unevenness of generation, which depends on extraneous factors. The disappointing part is that we have no influence on them. However, there is a partial solution to that problem—energy storage systems.
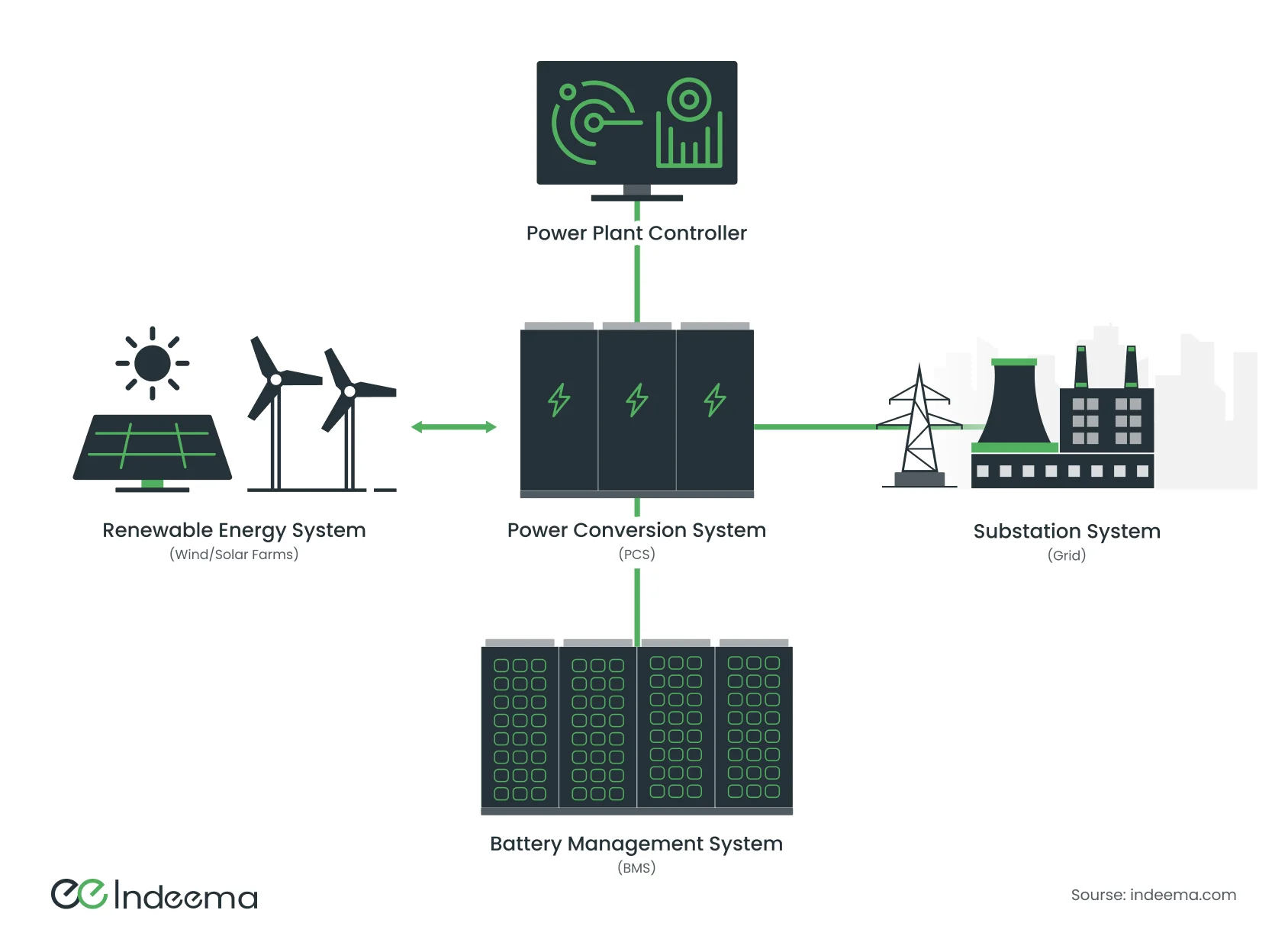
IoT systems can use external information, such as weather forecasts and near-future power consumption, to optimize the operation of generators and batteries. Some energy can be stored for later use so that users will have as much energy as they need, exactly when they need it.
2.2 Intelligent Electrical Power Distribution Systems
The Internet of Things also plays a huge role in determining data on power consumption by private households, enterprises, and other consumers. Of course, the main task of power meters for end users is to determine and control the cost of consumed resources.
By leveraging IoT technology, power distribution systems gain access to a wealth of real-time data on energy usage. Smart meters and sensors provide detailed insights into consumption patterns, allowing consumers and energy providers to better understand and manage their energy usage. AI algorithms, coupled with cloud-based data analysis, enable accurate consumption forecasting, identifying consumption trends, and providing valuable insights for optimizing energy usage.
For energy providers, IoT-driven power distribution systems offer enhanced efficiency in load management and demand response. Real-time data on consumption patterns allows for better load balancing, peak demand management, and proactive identification of potential issues or system failures.
2.3 IoT And Cloud-Based Power Consumption Monitoring
IoT allows you to know when and where energy is needed and where and how it is generated, but that isn't enough. Power must be delivered to users from power station. Energy IoT systems integrated into smart grids will be able to handle this load. Integrating these sensors in the transmission lines and transformers allows companies to collect real-time consumer consumption data.
Losses on the long-distance movement of power can reach 10%. Smart grids can optimize logistics and minimize the path from generation to the consumer along existing lines.
In addition, real-time data collection also allows turning off part of the lines or infrastructure in critical cases, for instance, when transformers are damaged, or power lines are broken. Immediate action in such cases helps to avoid fires or electric shocks and thus improves safety.
3. IoT Goes Green
Most of the renewable energies market is occupied by solar and wind power station. The symbiosis of Internet of Things solutions and new energy technologies creates new possible applications.
3.1 Harnessing the Sun: The Role of IoT in the Growing Solar Energy Revolution
For more than thirty years of the existence of solar energy, the cost of energy production through these resources has decreased almost a hundred times. In the next few years, this cost will decrease in price by another 8–15%.
More and more people are using solar panels to keep their smart home, security, and CCTV systems up and running continuously.
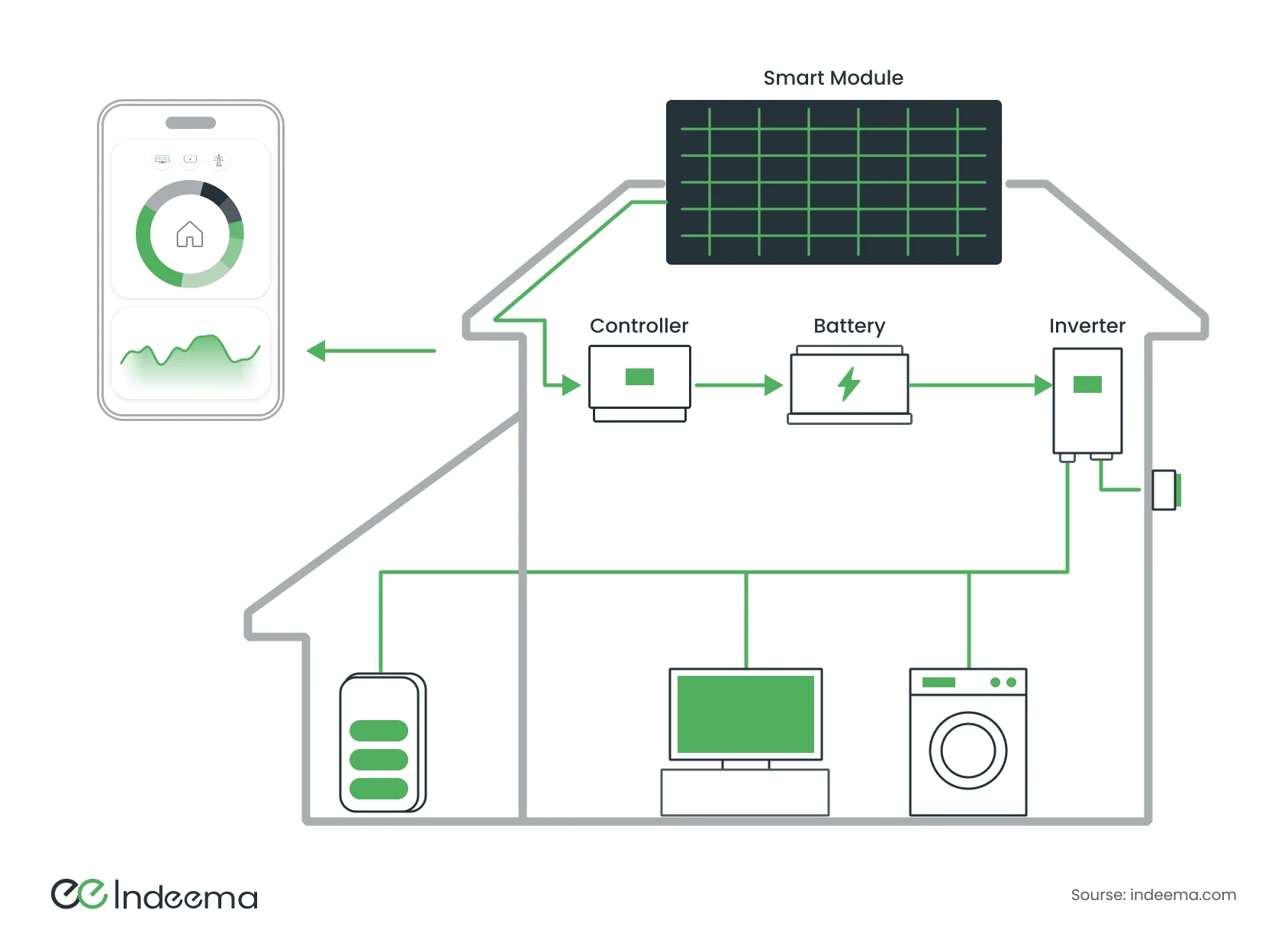
Also, home solar power plants are becoming more popular. These power station are sufficient for one household. They help users become energy independent and earn money by selling excess power to their energy suppliers.
Internet of Things in energy sector enables efficient use of clean energy by monitoring the condition of panels, batteries, and the power consumption of devices.
The use of IoT in large industrial solar power plants is indispensable because it solves the critical problems of energy companies:
- The efficiency of electricity generation by solar panels significantly depends on the angle of incidence of light rays on them. Therefore, continuous control of the inclination of the panels toward the sun is necessary. They have to behave like sunflowers to get the most. Control of the solar panels' dual-axis trackers relies, of course, on an IoT device.
- Solar power plants consist of many panels, which are responsible for collecting data on efficiency, temperature, etc. The IoT-based system determines inefficient, dirty, or misconfigured panels. Therefore, employees can check the status of only those panels that are not working properly without wasting time on others.
- Solar power plants occupy a large area with expensive panels and batteries, so there is a risk of common vandalism and theft. IoT sensors assist in providing quick alerts for any suspicious behavior in and around the power plant.
Solar renewable energy raise the degree of power-generating efficiency and support ongoing improvement.
3.2 IoT and Wind Energy: Unveiling New Horizons
The wind is the second-largest, inexhaustible resource for power generation. Modern wind turbines have high efficiency and long service life. However, the scale of the wind towers, as well as their separation from one another and smart cities, provide maintenance issues.
IoT devices with wireless data transmission can effectively determine the energy conversion efficiency, wind speed and direction, and the generating set and bearings condition.
In the same manner, as solar panels, intelligent systems save workers' time, optimize routes, and save expenses, but on a larger scale. Hence, IoT in renewable energy power production becomes irreplaceable again.
Moreover, engineers design wind power plants based on the data obtained from IoT devices.
Wind turbines cannot operate in light or very strong gusts. Firstly, there is simply not enough power to turn the blades. Secondly, there is a possibility of failure or even a crash. So, choosing the optimal remote location for new turbines is extremely critical.
On the basis of the large amount of data coming from IoT sensors, the system builds wind maps, which engineers use to find optimal locations for new renewable energy devices.
The close integration of the Internet of Things with renewable energy applications brings great efficiency and ensures incredible popularity worldwide.
Let Our Technology Experience Drive Your Business Forward.
4. Edge Computing And Smart Renewable Energy Systems
We emphasized that moving data processing closer to IoT devices significantly reduces latency when we talked about edge computing. In fact, delays are very important for sustainable energy systems; therefore, the recent trend is the integration of edge computing into power grids.
4.1 Edge IoT-Based Architectures
The architecture of solutions for smart grids is multi-layered. The bottom layer consists of various sensors that collect data on the state of energy resources, generation performance, network performance, power consumption, etc. All sensors are connected to the network using the next layer, on which various information transfer technologies work.
Clouds and Platforms are at the top of the tiered architecture, where essential computations, data storage, and artificial intelligence operations are performed. However, the Edge is becoming more prominent in a smart grid architecture between the network and the cloud.
Its use speeds up the system's response to rapid changes and unpredictable situations when the response of the operator or the cloud solution cannot be waited for. Edge IoT increases the resilience and flexibility of the system as a whole.
Another approach is the use of micro smart grids. A smart home, apartment, or building in the city can have its own power grid with access to local renewable energy devices. In this case, Edge IoT becomes the basis of the entire control system because the renewable energy generation and storage data are collected here.
IoT devices can control smart inverters and analyze and manage power consumption. The global power grid then acts as a virtual resource that can be interacted with in order to provide excess or consume insufficient power.
4.2 Power For The Edge
We mentioned the hassle of powering the sensors themselves, especially for remote systems like smart solar farms. Ensuring continuous operation of edge computing in a remote area is no less of a problem. Renewable energy applications can solve these issues.
Long power lines are unreliable and can be damaged by bad weather or icing. In circumstances where connectivity to the network can be supplied via satellite communication, the energy source must be local.
Small solar or wind generators are more efficient and reliable and may meet IoT devices' power needs. The application of renewable energy can also be effective for the backup power supply of edge servers at mobile communication stations in hard-to-reach areas.
Conclusion
Many industries have recently implemented IoT to increase productivity and effectiveness. Additionally, the energy sector is improving its sustainability by maximizing its utilization. Using standardized networks and protocols, the Internet of Things enables businesses to repair machine malfunctions remotely, manage their assets, and produce sustainable energy with optimal efficiency.
Undoubtedly, using renewable energy sources is the best choice for the future. They disintegrate entirely, resulting in negligible or no pollution and associated risks. Considering the promising future of renewable energy sources like geothermal, biogas, and hydroelectric power plants, it is imperative that these businesses implement IoT. As a result of the Internet of Things, eco-friendly goods can be manufactured and shipped in a dependable and financially viable manner.
Renewable Energy IoT Solutions With Indeema Software
If your business is looking to boost efficiency and provide more value to customers, Indeema Software can help with full-cycle energy software development. Expertise in AI and ML allows us to develop reliable energy industry solutions.
Get in touch with us today to talk with our specialists about how our IoT solutions can help your business save money on its energy bills.
Partner With Us and Leverage Our Technology Expertise.
