Introduction
The topic of IoT technology trends is no longer limited to just like-minded professionals, experts, and communities; it has become relevant and important for almost everyone in today's world. Being aware of IoT trends allows us to tap into new tools, platforms, and solutions that can greatly enhance both our personal and professional lives.
By staying up-to-date with the latest developments in IoT, we actively encourage knowledge sharing and learning from the experiences of others in the field. This collective wisdom helps us navigate the complex landscape of IoT, gain a broader perspective, and make more informed decisions.
As a result, the focus of this article will be on uncovering the top trends in IoT.
1. Definition of IoT and Its importance
IoT is not just a futuristic concept – it's a reality that's already transforming industries and changing the way businesses operate.
IoT, or the Internet of Things, is like a giant network where objects, like your home appliances (thermostat or refrigerator), or your entire manufacturing process, are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other.
It's like giving superpowers to ordinary things, making them smarter, more efficient, and able to work together to make your life easier and more convenient.
The benefits of IoT go beyond just operational efficiency. It also has the potential to create new revenue streams, enable innovative business models, and drive digital transformation.
Enterprises and large tech companies will play a critical role in shaping the future of IoT. By investing in IoT technologies, developing robust security and privacy protocols, and collaborating with stakeholders across industries and domains, they can unlock the full potential of IoT and drive sustainable growth, as well as shape Internet of Things future trends.
2. Overview of IoT Trends
With the rapid advancement and widespread adoption of IoT technologies across industries, a multitude of IoT trends can be found throughout the web. Yet, through meticulous analysis of enterprises and their strategies, we can discern the most remarkable IoT trends that are poised to redefine the future of businesses worldwide in the coming years. These trends hold the power to revolutionize operations, enhance efficiency, and unlock untapped opportunities, propelling organizations towards unprecedented levels of success and innovation.
2.1 Growth of Edge Computing in IoT
With edge computing, data processing and storage is done locally, at the edge of the network, closer to where the data is generated.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global edge computing market size is expected to grow from $44.7 billion in 2022 to $101.3 billion by 2027, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.8%. The report highlights the increasing adoption of IoT and proliferation of mobile devices, along with the growing demand for real-time computing and reduced latency, as the key drivers for the growth of edge computing.
Benefits of Edge Computing in IoT
Edge computing reduces the time it takes to process and analyze data, enabling real-time decision-making; provides reliable and continuous operation even in the absence of network connectivity or cloud access; provides additional security by keeping sensitive data closer to the source, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Use cases of Edge Computing in IoT
Some of the most common use cases for Edge Computing in IoT include: managing traffic flows, improving public safety, and optimising energy usage in smart cities; monitoring patients in real-time and reducing the need for hospitalisation; and monitoring soil quality, crop health, and weather patterns, enabling precision farming and reducing waste.
Explore Our Success Stories.
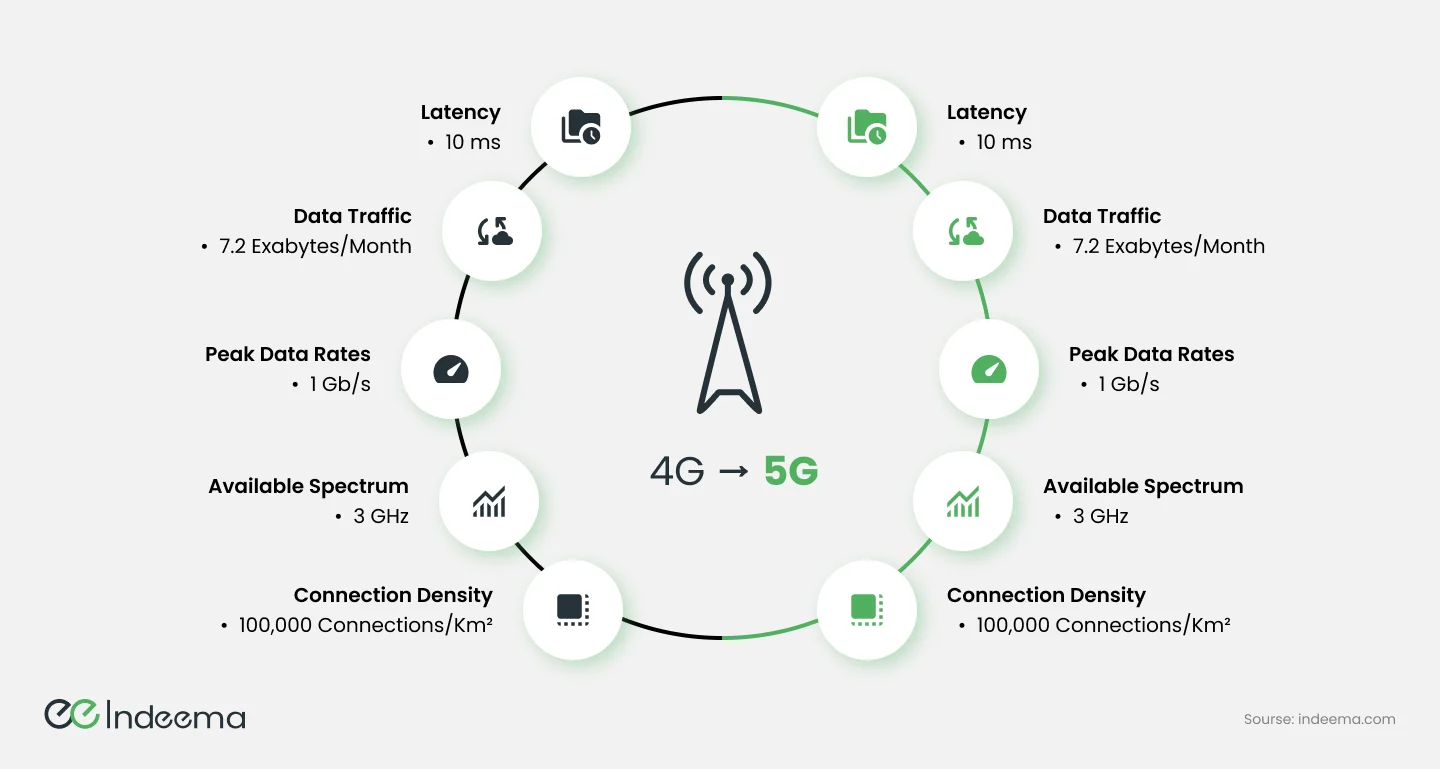
2.2 Emergence of 5G Networks in IoT
5G networks, or fifth-generation networks, represent the latest and most advanced generation of mobile telecommunications technology. They are designed to deliver faster speeds, ultra-low latency, massive connectivity, and high reliability compared to their predecessors. Unlike previous generations, 5G networks support a wide range of IoT devices, enabling seamless communication between devices and unlocking unprecedented possibilities.
Benefits of 5G Networks in IoT
The ultra-low latency provided by 5G networks enables near-instantaneous communication between devices. This opens up new possibilities for time-critical applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and smart grids, where even the slightest delay can have significant consequences.
5G networks can support a massive number of connected devices simultaneously, thanks to their enhanced capacity. This capacity expansion enables the seamless integration of IoT devices at a large scale
Use cases of 5G Networks in IoT
In the industrial sector, 5G networks in IoT drive the implementation of advanced automation and optimization. With reliable and low-latency connections, manufacturers can deploy IoT devices to monitor equipment performance, optimize processes, and enable predictive maintenance, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
5G networks in IoT transform transportation and logistics by enabling connected and autonomous vehicles, intelligent traffic management, and efficient supply chain operations. These technologies enhance road safety, optimize traffic flow, and enable real-time tracking of goods, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced costs.
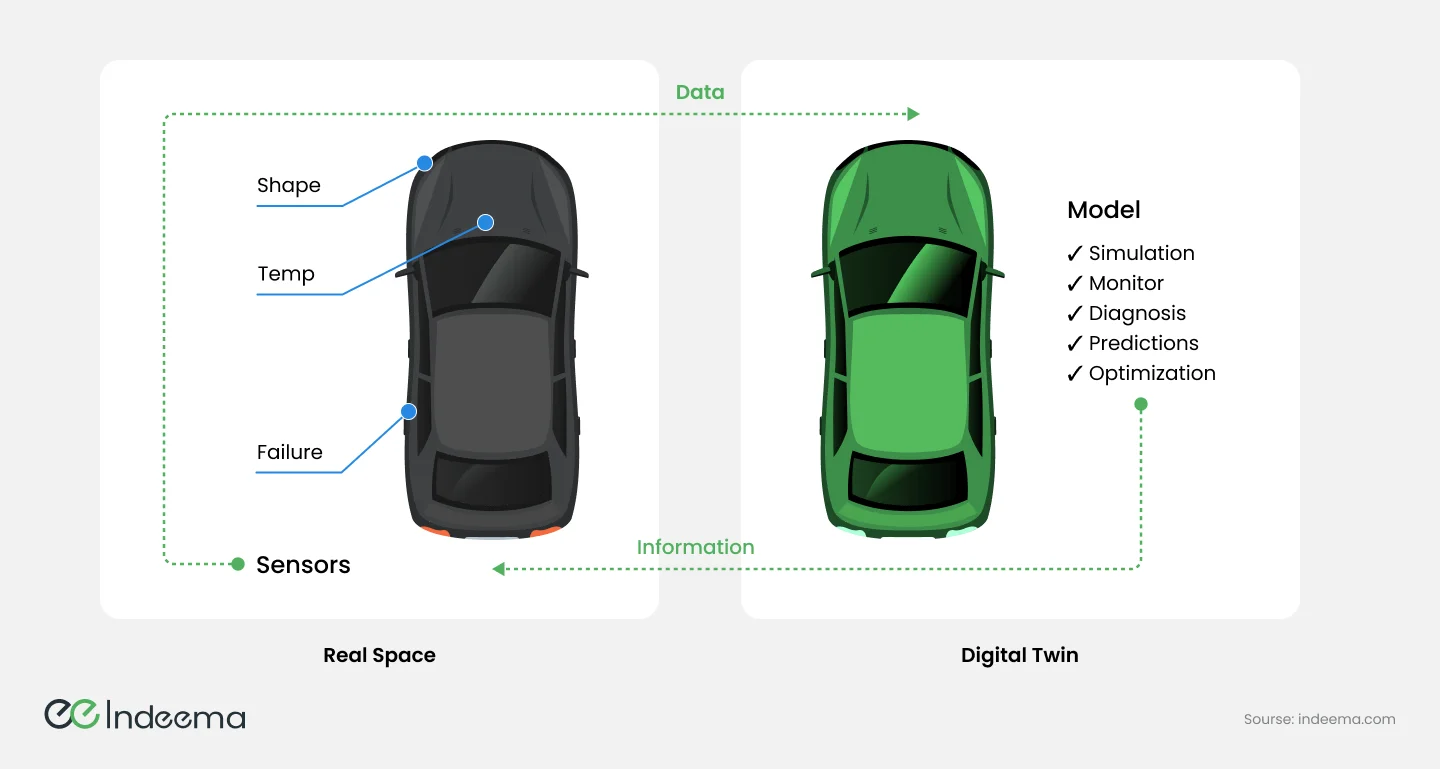
2.3 Digital Twins
Digital Twins technology is considered a part of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. It relies on sensors, data collection, and data analysis, which are key components of the IoT. Digital Twins create a virtual replica of a physical object, process, or system, that can be monitored and optimized using real-time data collected through IoT sensors.
Benefits of Digital Twins
By using real-time data from IoT-enabled devices, equipment, and systems, companies can identify areas of waste, reduce downtime, and optimize resource utilization. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved efficiency.
Use cases of Digital Twins
Digital Twins technology, for example, is widely used in the automotive industry to simulate and test new vehicle designs before physical prototypes are built; to imitate and test autonomous driving systems, aiding in their accuracy and safety; and to monitor the entire supply chain, from manufacturing to delivery, in order to optimize logistics and reduce costs.
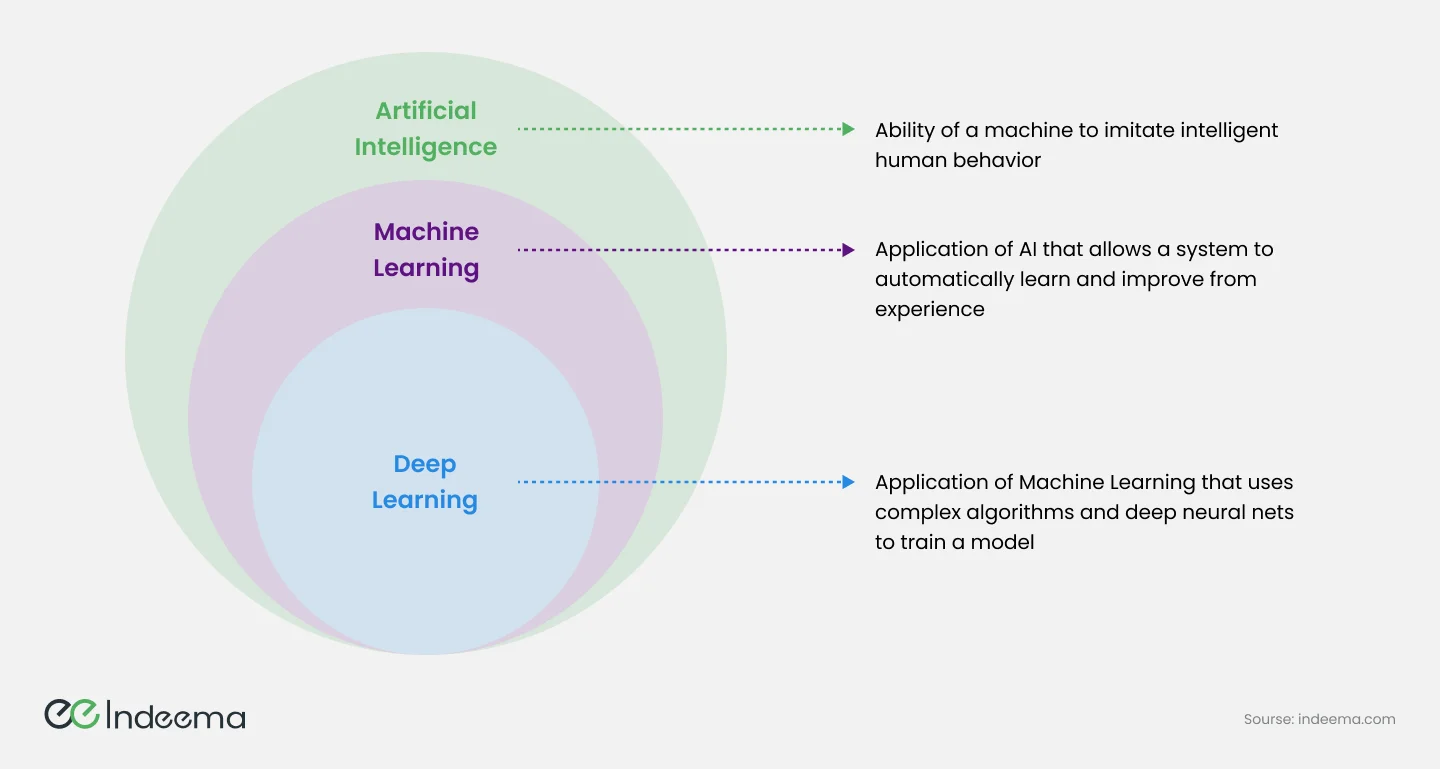
2.4 Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for IoT
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to develop intelligent machines that can mimic human intelligence. Algorithms, data analysis, and pattern recognition are used by these systems to make informed decisions and solve complex problems. A subset of AI known as Machine Learning focuses on teaching computer systems to learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed.
According to market research, the global AI in IoT market is expected to reach a value of USD 20.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of over 26%.
Benefits of AI and Machine Learning in IoT
Integrating AI and machine learning with IoT devices enables intelligent automation. Learning from historical data, ML algorithms can make autonomous decisions to optimize operations, reduce energy consumption, and streamline processes. AI and ML algorithms can also monitor IoT-generated data streams in real time, detecting deviations from expected patterns.
These technologies also enable IoT devices to learn and adapt to individual user preferences, resulting in more personalized experiences. AI-powered IoT systems can personalize recommendations, adjust settings, and anticipate user needs, increasing convenience and satisfaction.
Use cases of AI and Machine Learning in IoT
AI-powered IoT devices create intelligent, comfortable, and energy-efficient living spaces by controlling lighting, temperature, and security systems, as well as managing appliances and optimizing energy usage.
AI and ML models can detect patterns indicative of impending failures by analyzing sensor data from industrial equipment. This allows for proactive maintenance, which reduces downtime and improves equipment performance.
IoT systems powered by AI also help with efficient fleet management, logistics optimization, and intelligent transportation infrastructure.
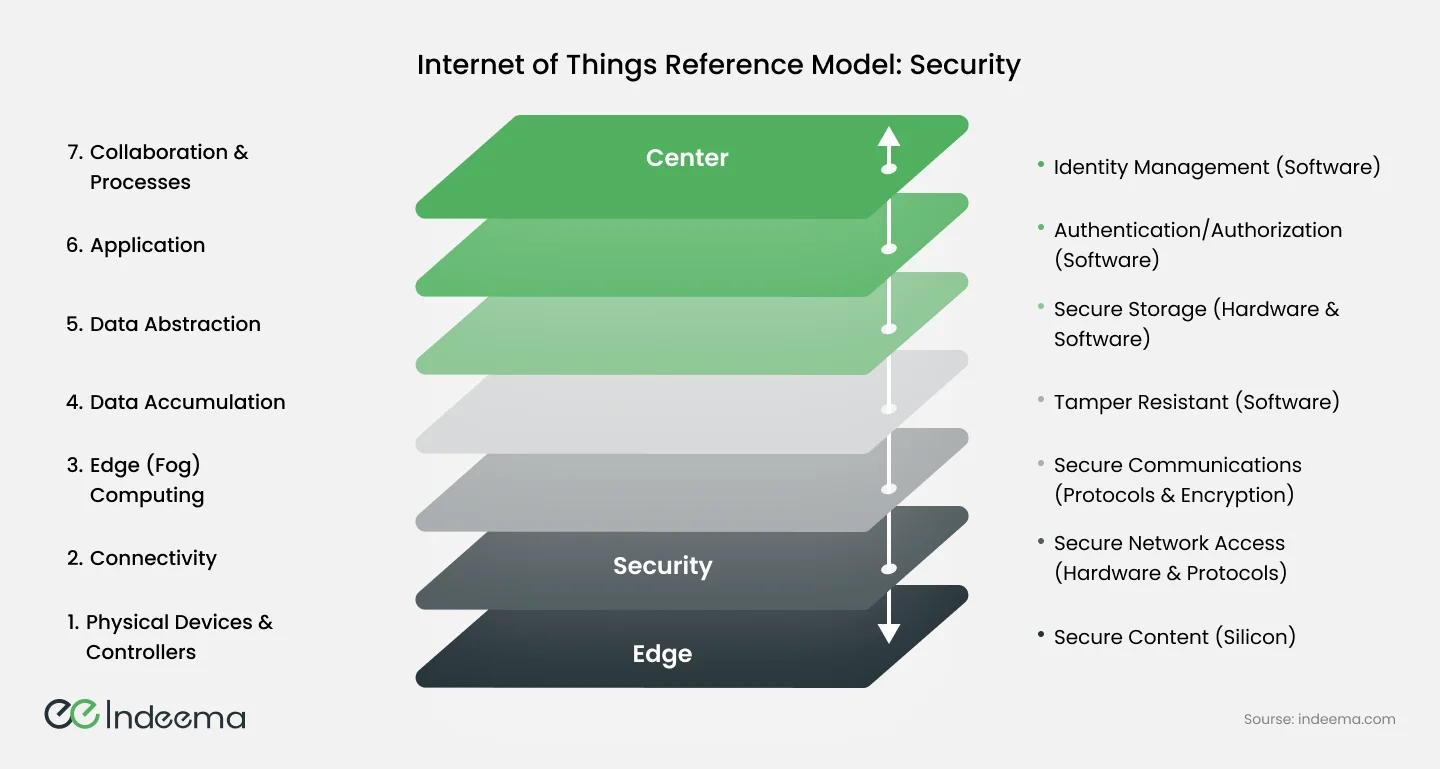
2.5 Security and Privacy Concerns in IoT
Overview of Security and Privacy Concerns in IoT
Vulnerabilities in Devices: IoT devices frequently have limited computing resources and lack robust security features. As a result, they are vulnerable to attacks like unauthorized access, malware injection, and data breaches. Compromised devices can be used by hackers to gain access to sensitive data or launch larger-scale attacks.
Data Privacy: IoT devices collect and transmit massive amounts of personal data, raising privacy and data protection concerns. Because of the interconnected nature of the IoT, there is a risk of unauthorized access, data interception, and misuse of personal information. Unauthorized access to sensitive data can result in identity theft, surveillance, and privacy violations.
Lack of Standardization: The absence of universal security standards and protocols across IoT devices poses a challenge. Different manufacturers may implement varying security measures, making it difficult to ensure a consistent level of security across the IoT ecosystem. This lack of standardization creates vulnerabilities and impedes effective security management.
Solutions to Security and Privacy Concerns in IoT
Strong Authentication and Encryption: Implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication and secure encryption protocols, helps ensure the integrity of IoT device communications. Strong authentication prevents unauthorized access, while encryption protects data in transit and at rest, safeguarding privacy.
Regular Security Updates: IoT device manufacturers should provide timely security updates and patches to address vulnerabilities. Regular updates help protect against emerging threats and ensure devices have the latest security enhancements. Manufacturers should establish mechanisms for seamless and automatic updates to mitigate security risks.
Privacy by Design: Privacy considerations should be incorporated into the design and implementation of IoT devices and systems. Adopting a privacy-by-design approach ensures that privacy features are embedded from the outset, and it is likely to be one of the key internet of things future trends. This includes minimizing data collection, providing user consent mechanisms, and enabling granular control over data sharing.
Industry Collaboration and Standards: Stakeholders across the IoT ecosystem, including manufacturers, policymakers, and researchers, should collaborate to establish industry-wide security standards and best practices. Promoting standardization and knowledge sharing enhances security measures, ensures interoperability, and fosters a more secure and privacy-focused IoT environment.
3. IoT's Resilient Stance in an Economic Downturn
According to the January 2023 update of IoT Analytics' Global IoT Enterprise Spending Dashboard, despite a decline in overall IT spending in 2022 and a slow growth projection for 2023, the enterprise IoT sector remains resilient, with a 19% growth rate expected in 2023.
While hundreds of layoff announcements have occurred in the technology industry, affecting over 95,000 employees as of early February 2023, the impact on IoT-related job roles has been relatively limited. Instead, companies like Schneider Electric see this as an opportunity to hire highly skilled and experienced workers, taking advantage of the tech shake-up to alleviate labour shortages and accelerate their digital transformation efforts.
The IoT enterprise market has a strong long-term growth potential and is expected to reach $484 billion by 2027.
Let Our Client Success Stories Inspire You.
Conclusion
We have explored the various facets of the top IoT trends in 2023. With edge computing optimizing data processing, 5G networks revolutionizing connectivity, digital twins enhancing efficiency, and AI and machine learning driving intelligent decision-making, IoT continues to reshape industries and improve lives.
Despite economic downturns, the resilience of the IoT has shone through. It has proven its ability to adapt, innovate, and thrive amidst challenging times. The journey of the IoT is just beginning, and the opportunities ahead are boundless.
